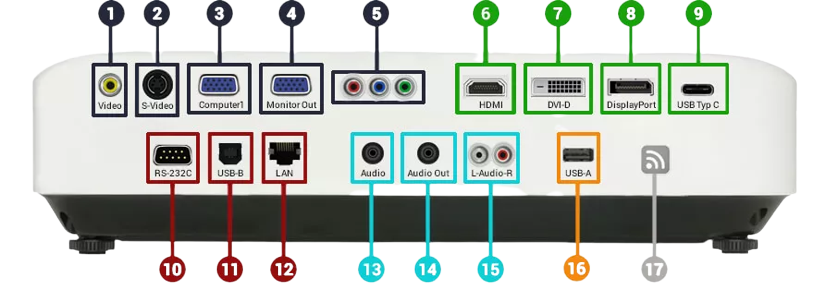
Connectivity
Signal Management Equipment for Conference Room and Home Cinema
To make your choice easier, we have compiled the most important criteria and information about high-quality signal transmission. This way you know what is important before you buy!
Cables and adapters for every application
Do you have a good connection to your projector, PC or hi-fi equipment? If not, we have suitable cables and adapters for you to exploit the full performance of your devices.
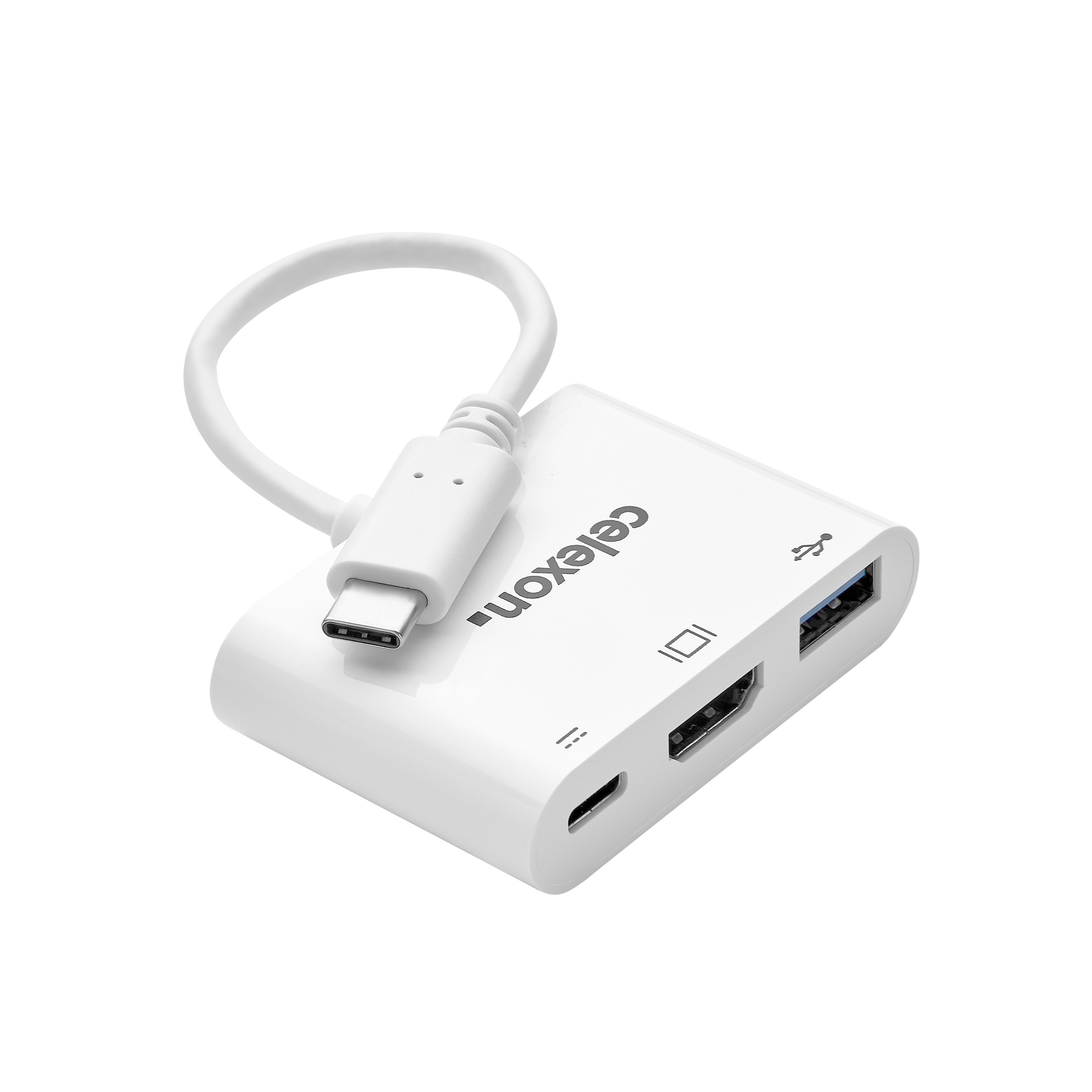
If components in your system do not fit together, appropriate adapters can help to connect your devices. We have a large selection of adapters for various interfaces.
Reliable connections to projectors, displays or monitors are thus guaranteed. Of course, our contact persons will also be happy to advise you personally on your purchase! Discover high-quality cables and adapters for home cinema, conference room or home office now.
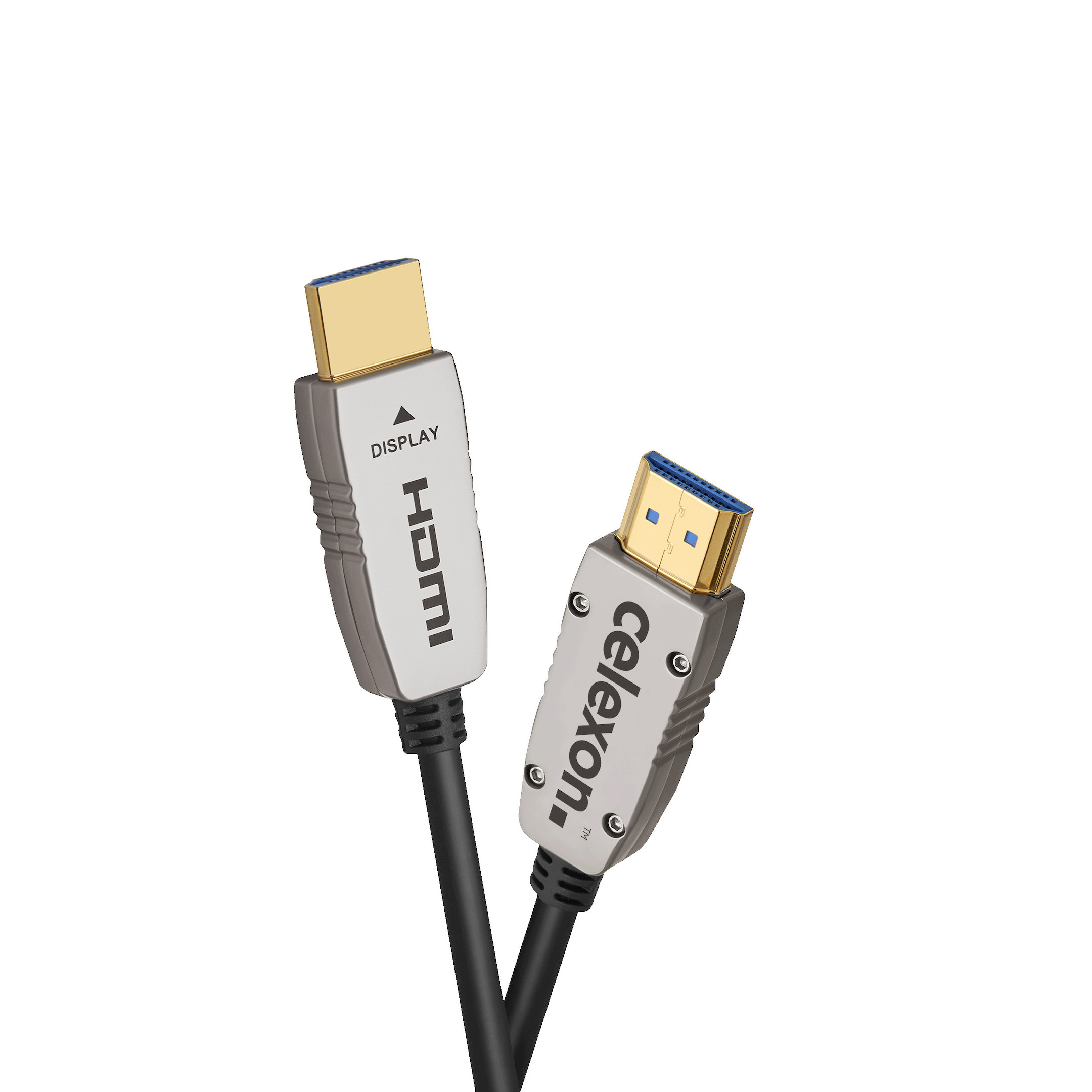
HDMI cable: Everything you should know before buying
The HDMI cable is the most popular and well-known type of cable among multimedia cables. In addition to connecting different devices, it is used to transmit digital audio and video signals. HDMI ports are available on most modern laptops and tablets. They provide a convenient way to connect your devices to a display or monitor. When using HDMI cables, no additional cables (e.g. separate audio cables) are needed.
When buying an HDMI cable, you should consider these 4 criteria:
1. HDMI cable designations
| Maximum data rate | Maximum image resolution | Frame rate | |
| HDMI 1.0 HDMI Standard | 4,95 GBit/s | 1080p | 60 Hertz |
| HDMI 1.4 HDMI-High-Speed | Type A and C: 10,2 Gigabit | 2160p | 120 Hertz |
| HDMI 2.0 HDMI-High-Speed Premium | 2160p, 60 Hertz | 2160p, 60 Hertz | 120 Hertz |
| HDMI 2.1 HDMI Ultra High Speed | Type A, C and D: 38 Gigabit | 4320p, 60 Hertz | 120 Hertz |
2. The main HDMI connector types and what they are used for
3. Cable shielding for best possible sound and picture quality
Well-shielded HDMI cables are insensitive to external electrical and magnetic fields. This means you maintain the best possible sound and picture quality. As a rule, the more layers of sheathing a cable has, the better it is protected.
4. HDMI cable length
Cable lengths of 1 to 10 metres are common. If the HDMI cable is too long, it should be noted that the signal strength decreases as the attenuation increases. For cable lengths over 10 metres, an HDMI amplifier / repeater or hybrid fibre optic cable should be used to amplify the signal. With the help of a connection standard HDBaseT, you can transmit HDMI signals over a distance of up to 100 metres.
Our tip
HDMI also works without cables. With a corresponding wireless HDMI system, you can transmit high-definition content wirelessly. If your projector or monitor is equipped with an older DVI connection, you can use an HDMI adapter to establish a connection via an HDMI cable.
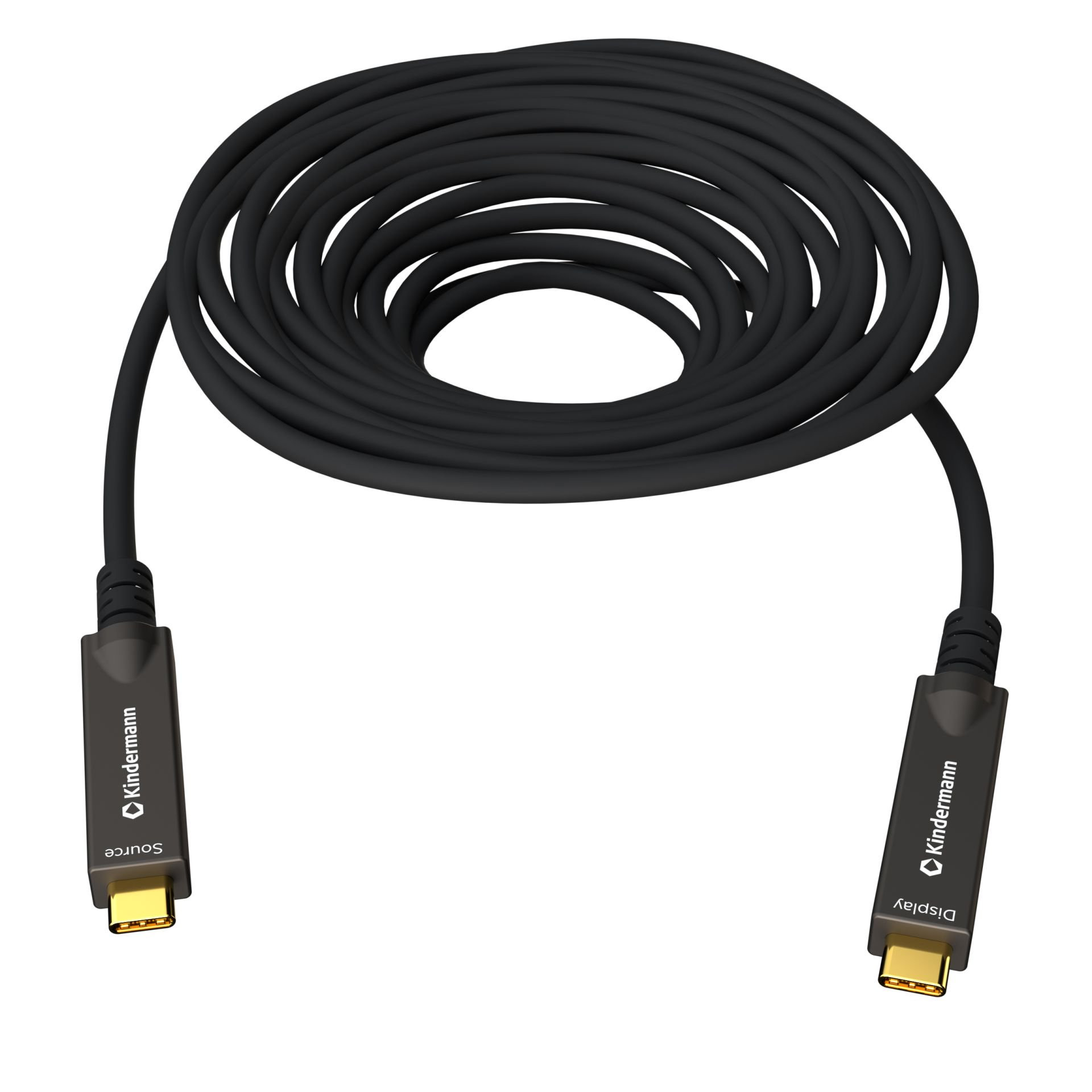
DisplayPort cable: What is it?
DisplayPort is comparable to the HDMI interface and belongs to the digital transmission standard for image and sound. While HDMI provides for the connection of multimedia and home entertainment devices, the DisplayPort is predominantly used for transmission from a computer or notebook to a monitor. A major advantage of DisplayPort technology is that large amounts of data can be transmitted in a small space. This makes them ideal for space-saving integration into smaller electronic devices such as tablets, notebooks and computers.
A DisplayPort connector comes in two versions:
Our tip
Does your PC have a DVI or HDMI interface, but no DisplayPort output? No problem: To adapt different connections to DisplayPort, we have suitable DisplayPort adapters for you.
DisplayPort vs. HDMI: Where are the differences?
Anyone who has ever connected their computer to a monitor will have asked themselves which interface is ideally used to connect these two devices. In addition to HDMI plugs, many devices also have DisplayPort sockets. But which connection is better, DisplayPort or HDMI?
| DisplayPort | HDMI | |
| Mechanical locking | has an additional safety device | - |
| Cable length | up to 15 metres | up to 50 metres (above 10 metres amplifier necessary) |
| Colour depth | 30 bit per pixel | 48 bit per pixel |
| Network connection | - | Ethernet data transmission |
| Daisy chains | Connect multiple monitors in series | - |
| Compatibility | Compatible with VGA and USB-C | - |
| Sync programmes | NVIDIA G-Sync & AMDs Freesync | AMDs Freesync |
| Transmission of input commands | - | Transmission of control commands through HDMI-CEC |
| Audio Return Channel (ARC) | - | is supported |
Application areas of DisplayPort and HDMI
Our tip
Make sure that the source and the display device are of the same generation so as not to slow down the data transfer.
Connecting a projector with the right cable
If you want to connect a projector, the right cable is crucial. In order to bring order into the cable tangle, we explain the meaning and function of all possible connections of a projector. This way, you know what to look out for before you buy a projector so that you can enjoy the full projection pleasure.
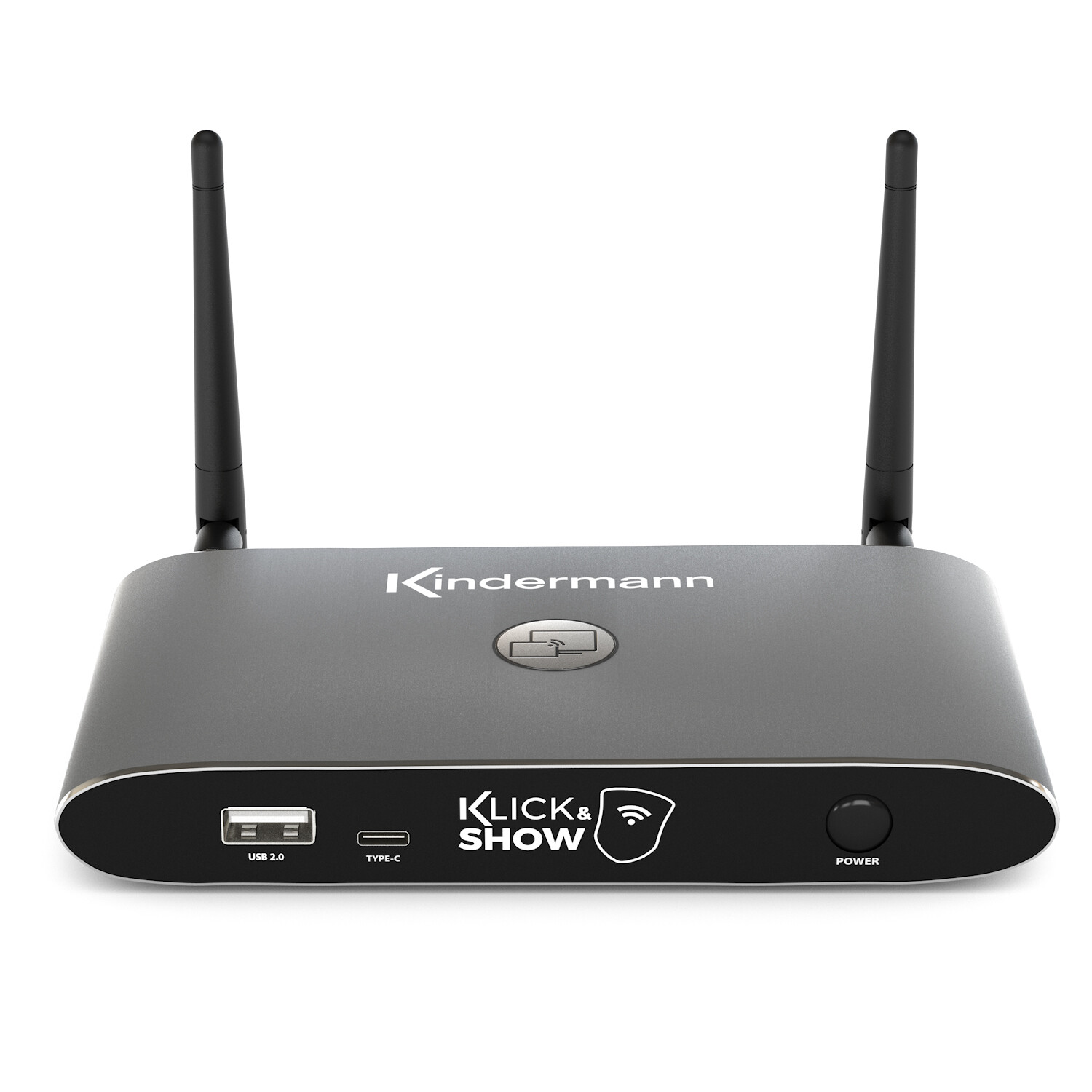
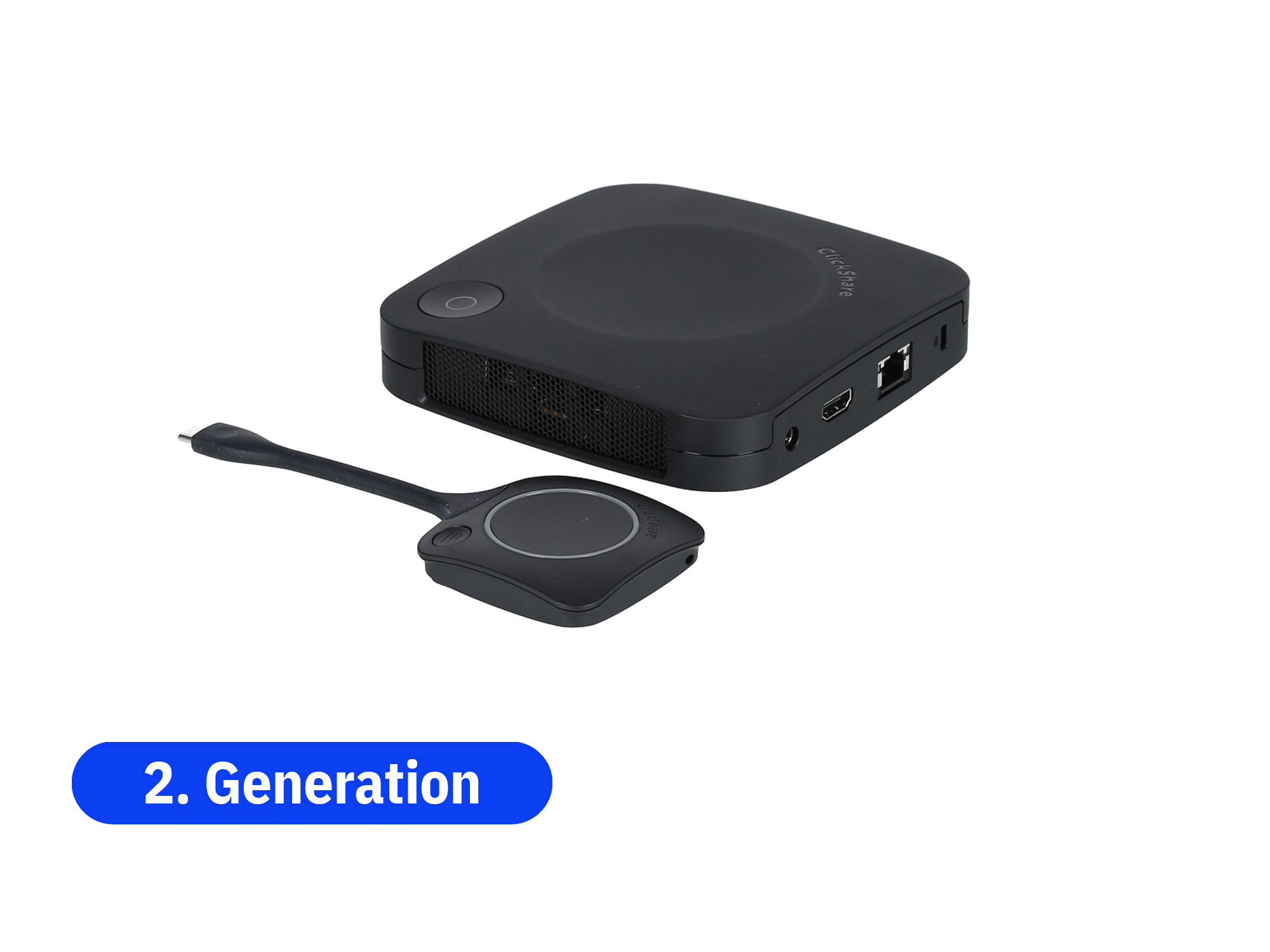
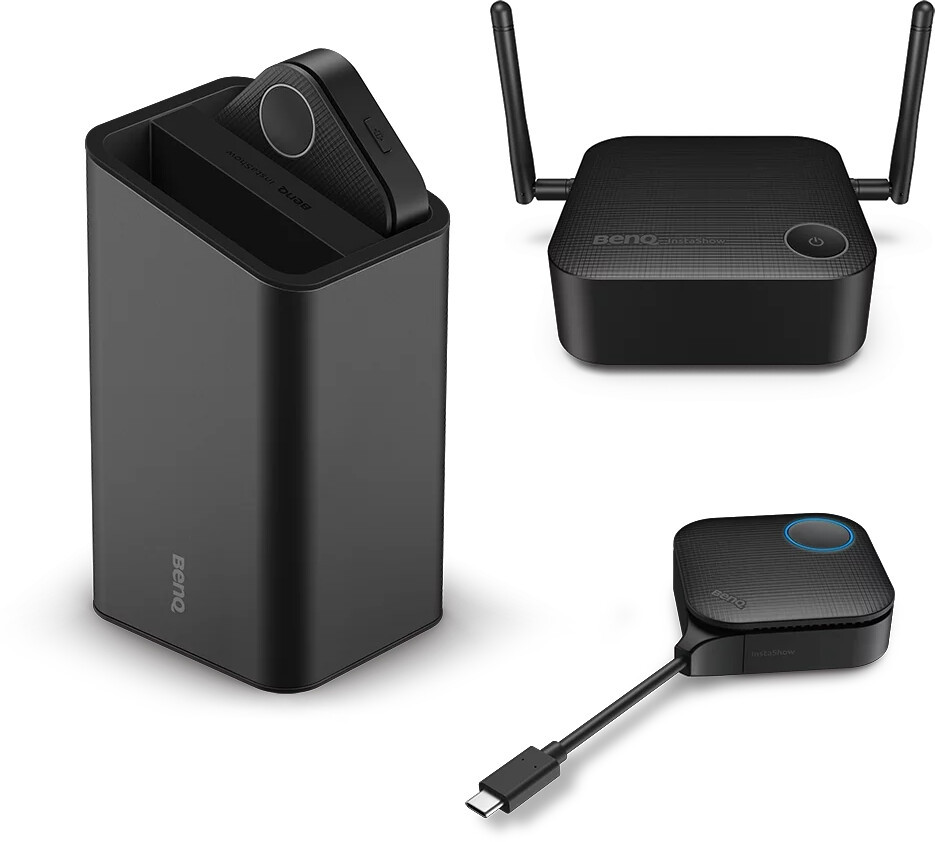
Wireless HDMI and Presentation - flexible presentation of your content
Wireless presentation systems are becoming increasingly important for signal management in meeting and conference rooms. With wireless HDMI and presentation solutions, you can quickly and flexibly transmit content from your laptop or smartphone to a central screen. Wireless presentation systems are easy to use, affordable and convenient. Presenting your content in meetings or conferences will be easier than ever before!
Our tip
If you want to start your presentations without cables, take a look at our wireless presentation systems. With the plug-and-play solutions, your content is transmitted wirelessly from the screen, tablet or notebook to a presentation screen in the meeting room.
Network - routers and access points for perfect signal strength
Routers and access points are part of the basic Internet equipment, especially for larger facilities and offices. These ensure a stable and interference-free WLAN within your network. Wherever you want to improve the speed and performance of your wireless network, routers and access points can be set up.