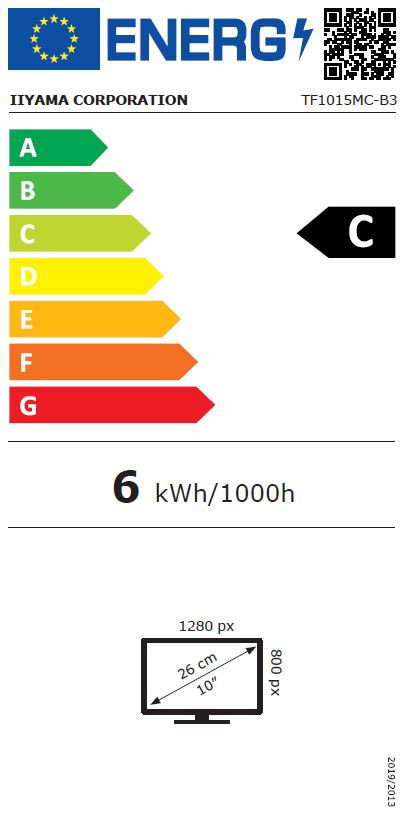
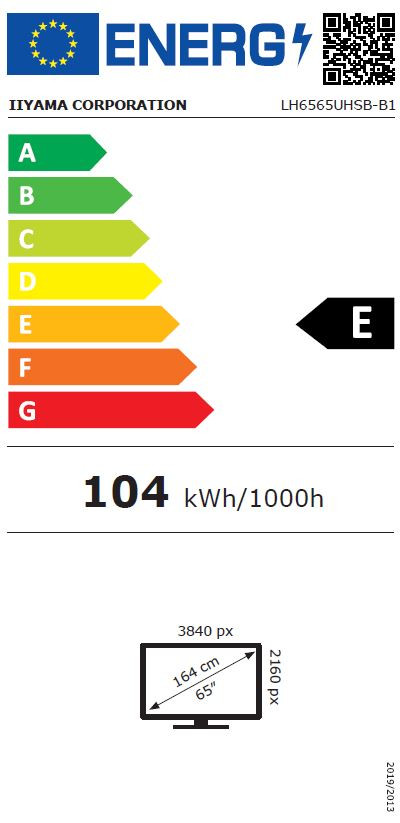
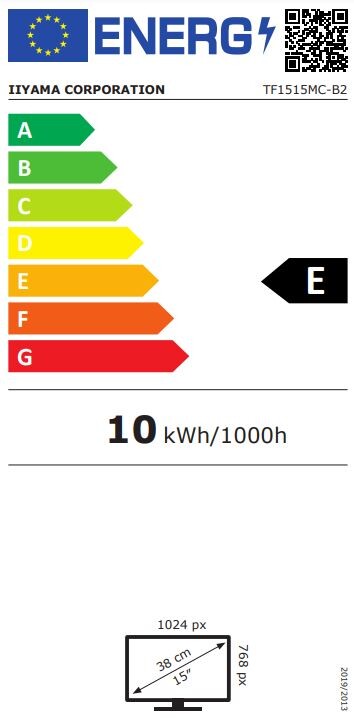
Displays
Here you will find professional digital signage displays as well as interactive touch displays, video wall displays and even LED walls for indoor and outdoor use. We also offer numerous display accessories such as signage players and various display mounting systems.
Are you looking for an individual solution for a conference room, meeting room or point-of-sale? Our visunext product experts will be happy to help!
Displays for every field of application
Displays have long since become part of our everyday lives - both at work and at home. We receive a wide variety of information via displays everywhere: the latest offers, infotainment, but also company and project presentations as well as the contents of seminars and training courses.
There are suitable display solutions for almost every area of application. We have displays for every area of application and in every price range.
What is important when buying a display?
If you already know how and where you want to use displays, then orientation is comparatively easy. There are just a few tips and important technical display features we would like to share with you that you should definitely know.
Image resolution
The image resolution of a display is one of the most important properties. This is because, in addition to contrast, brightness and viewing angle stability, it ultimately determines the image quality of a display.
The most popular image resolutions for displays are Full HD (1,920 x 1,080) and 4K UHD. In principle, we recommend 4K UHD over Full HD image resolution, especially for displays with a larger screen diagonal. The reason for this is the usually short viewing distance: the image of a 4K display simply looks more high-resolution and thus also significantly better than the image of a Full HD display for a viewer who is at a short distance from the display.

Brightness
The brightness of a display is at least as important as its image resolution. As with monitors, this is expressed in candela (cd/m²), or more rarely, in nit (nit). The value of the two units of measurement is the same. This means that 500 cd/m² correspond to 500 Nit and vice versa.
How bright a display needs to be depends on where you want to use it and how strong the ambient light is.
| Light intensity | Application situation |
| approx. 350-450cd/m² | Rooms with controllable lighting conditions |
| from 500 cd/m² | Normal ambient lighting conditions |
| approx. 700 cd/m² | Strong ambient light, but no direct sunlight (e.g. reception hall) |
| from 700 cd/m² | Very bright environment, direct sunlight (e.g. shop window, outdoor)
|
Contrast
When we talk about contrast, we usually mean brightness contrast, or more precisely: the ratio between the darkest and the brightest point of an image. The greater this ratio, the more attractive and sharper the image appears to us. On most displays, the contrast is in the four-digit range. Common values are, for example, 3,000:1 and 5,000:1. Generally, many displays are comparable in terms of contrast. Both displays with a contrast of 3,000:1 and displays with the 5,000:1 contrast show a very similar, solid image.
Viewing angle stability
Viewing angle stability is the property of display panels that refers to the maximum possible viewing angle at which the displayed image can be shown to the viewer with little or no loss of image quality. The greater this angle, the weaker the loss of quality in terms of colour representation and brightness.
Displays with stable viewing angles usually have a maximum viewing angle in the horizontal plane of between 160 and just under 180 degrees.
Runtime
The runtime release is the suitability of a display for continuous operation. The specification for this is made up of the maximum number of hours per day in relation to the duration of a week. As a rule, displays for professional use are designed for 24/7, 16/7 or 12/7 continuous operation. Of course, other specifications such as 10/7 can also be found. In our table, you will find the typical operating times for the respective operating duration.
| Runtime approval | Best suited for |
| 24/7 | Deployment around the clock |
| 16/7 | Deployment beyond one working day |
| 12/7 | Deployment during business hours |
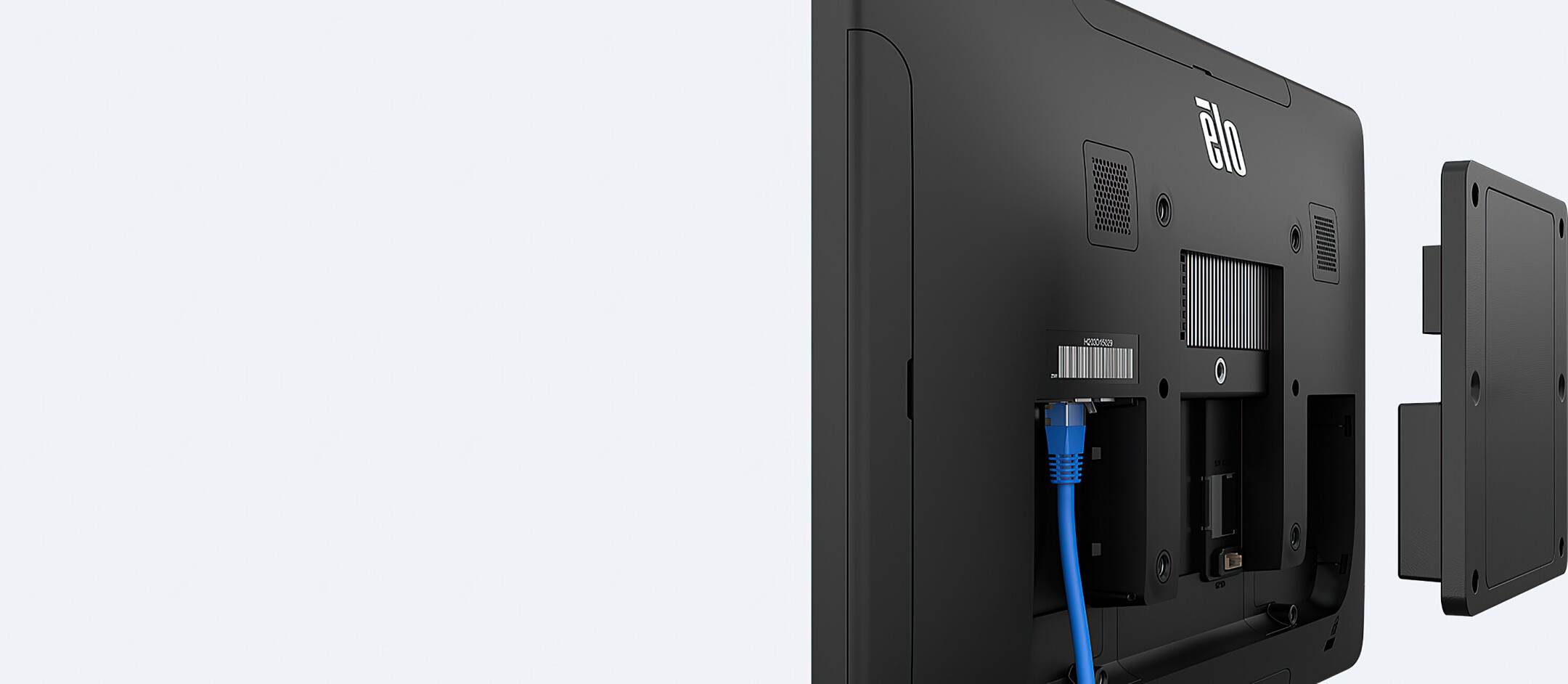
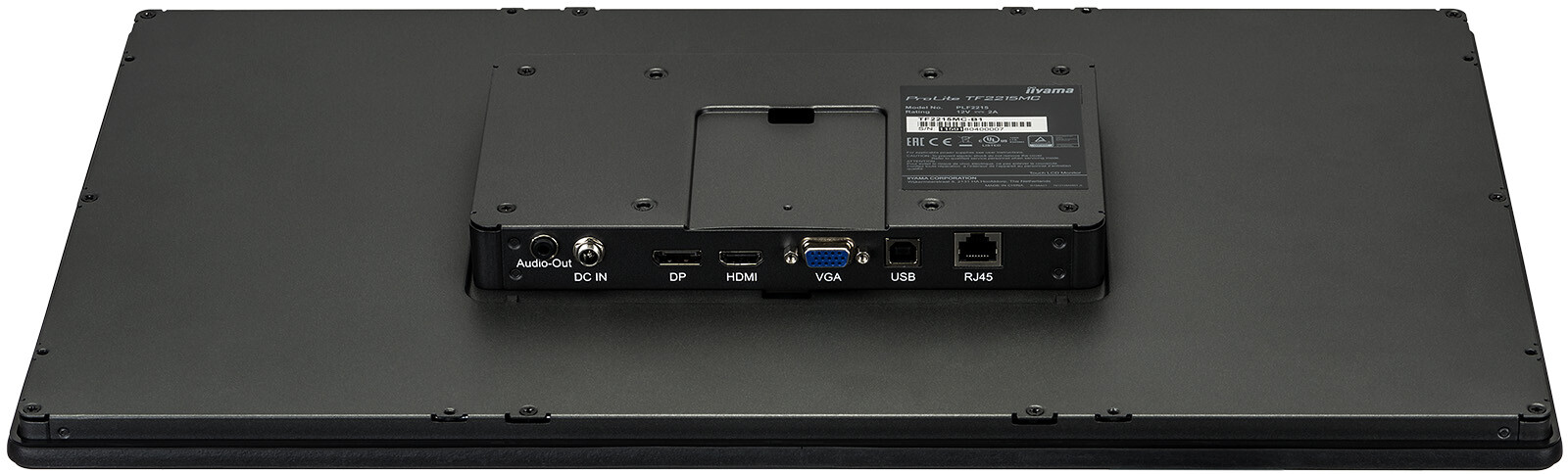
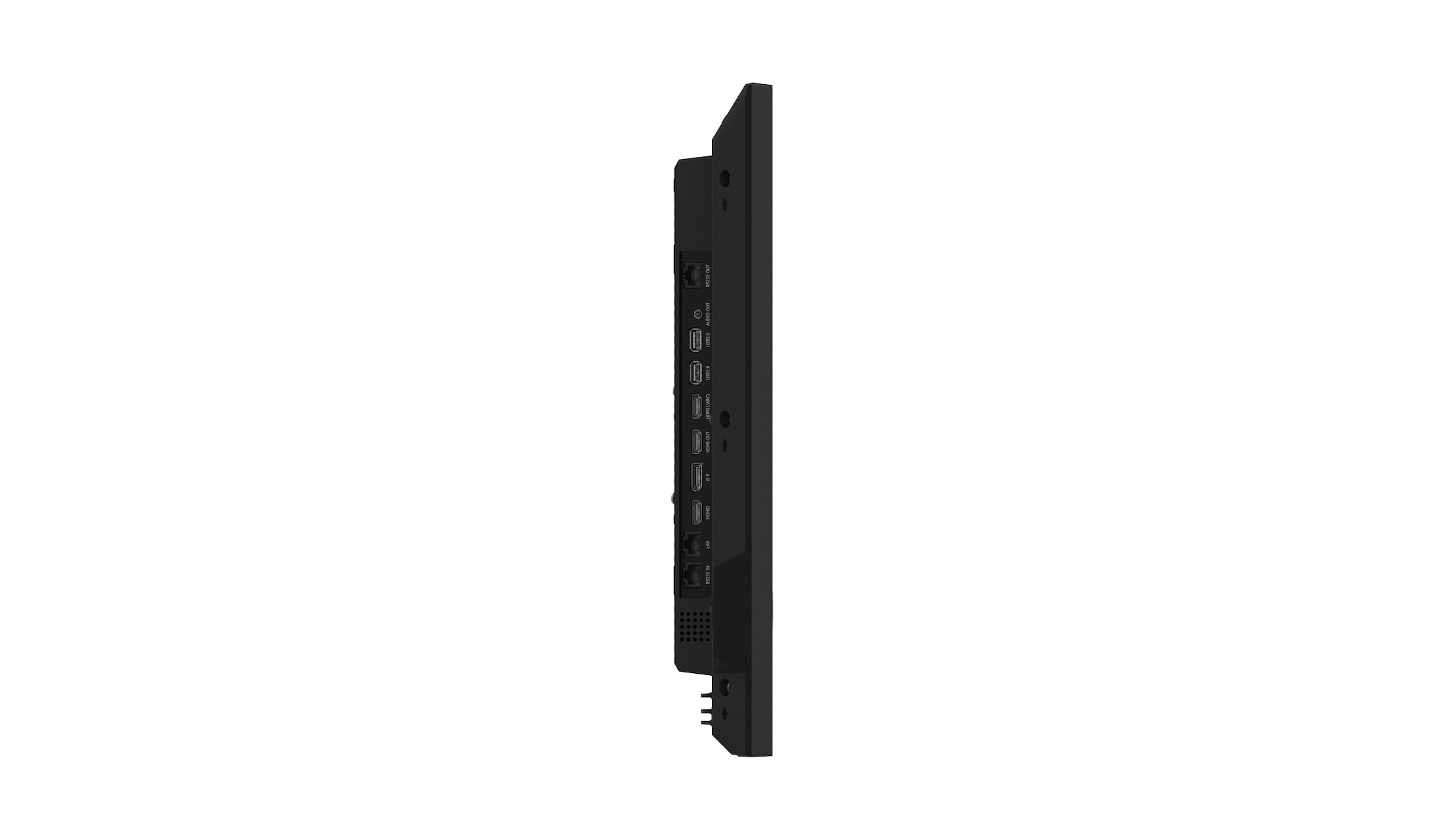
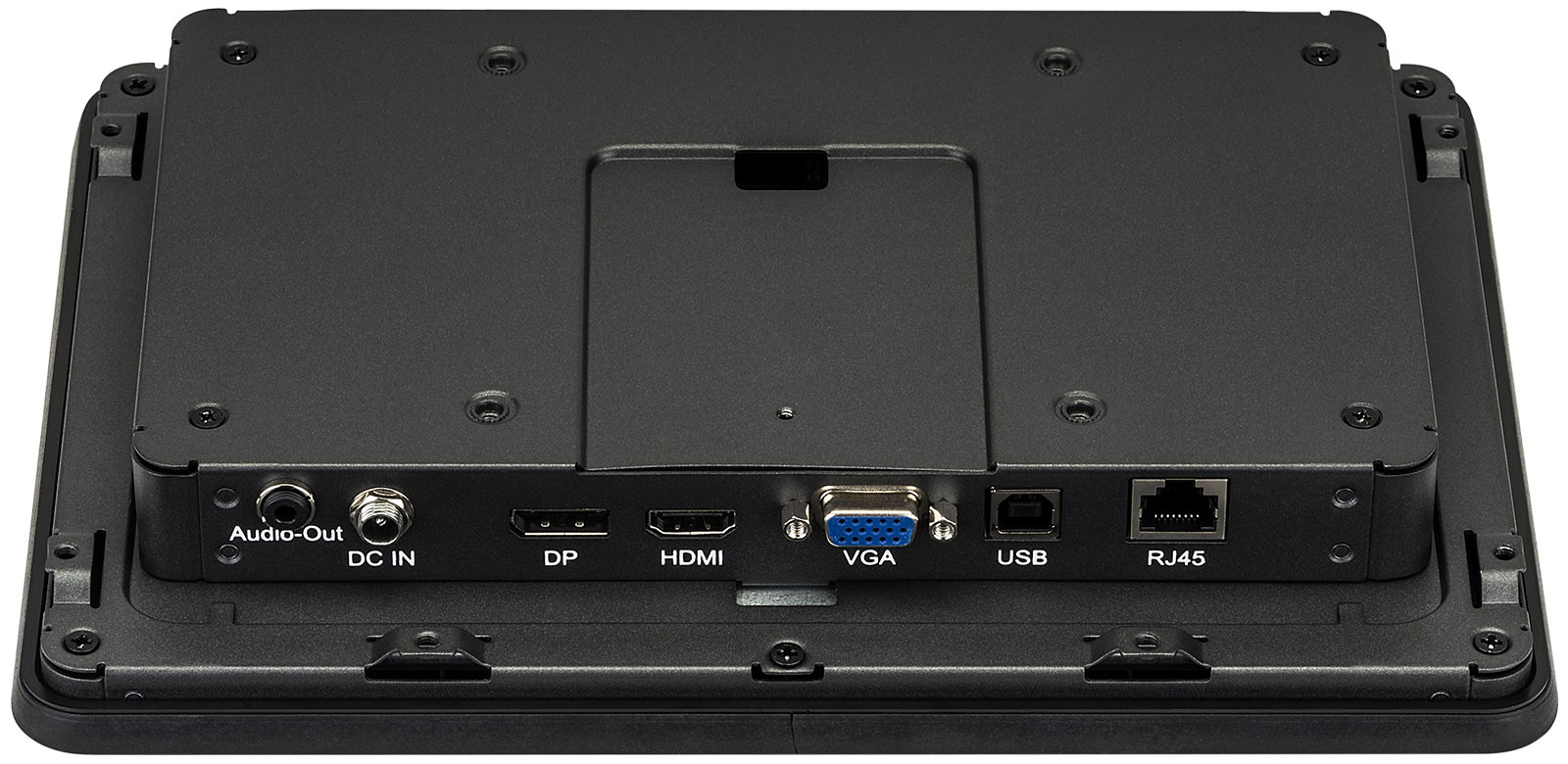
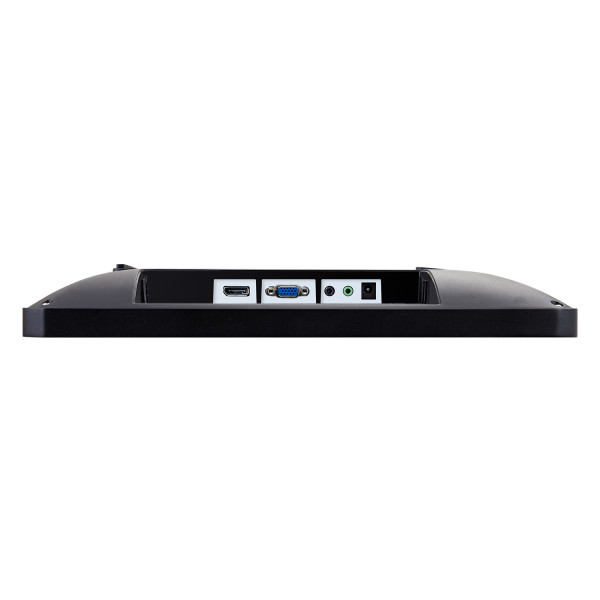
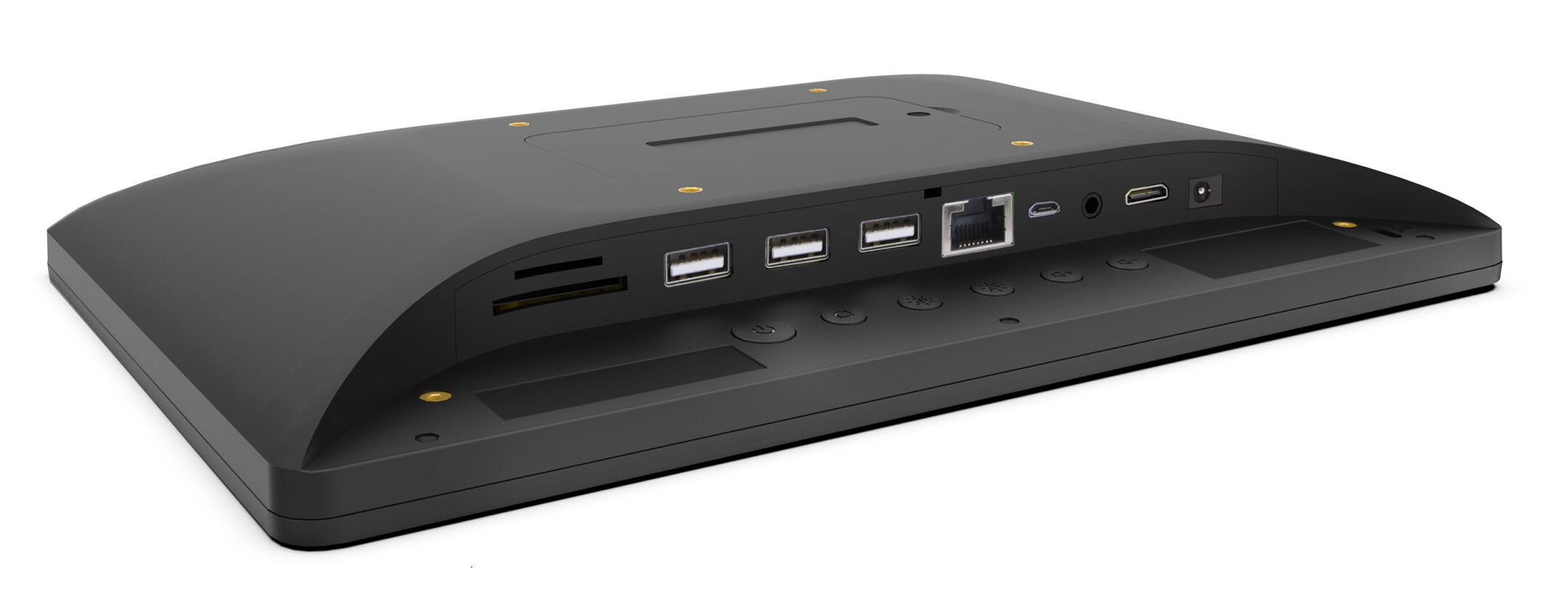
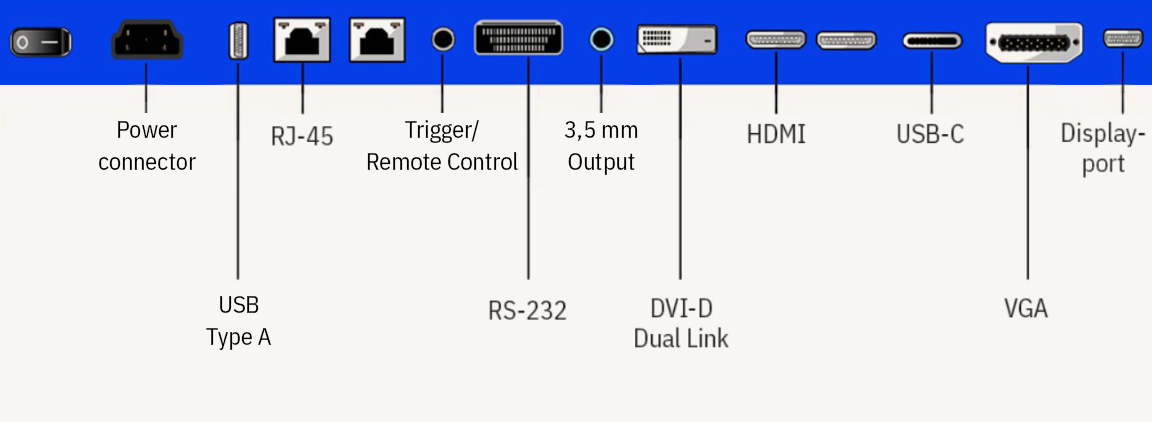
Connectors
The most frequently used display connections include HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort and VGA. The HDMI connection is by far the most frequently used in practice. This is because the transmission standard of the HDMI connection is designed for the simultaneous transmission of the audio and video signal. In addition, the HDMI standard also supports the transmission of 4K content. Alternatively, you can also use the modern DisplayPort connection, if available.
DVI and VGA are pure video connections. In addition, the feed via VGA is only analogue, which is why you should rather use an HDMI connection.
Additional connections are interfaces for external control systems such as RJ-45 (LAN) and RS-232 interfaces. Often the displays also have a 3.5 mm jack output and one or more USB ports.
Mounting
There are usually different options for mounting a display: You can install a display either on a wall mount, ceiling mount or on a display stand. Depending on the area of application and room situation, you can choose the respective solution.
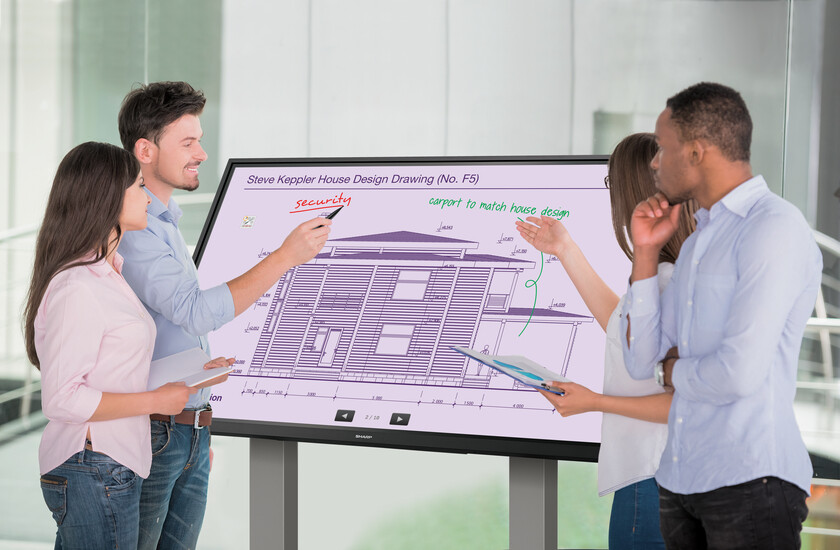
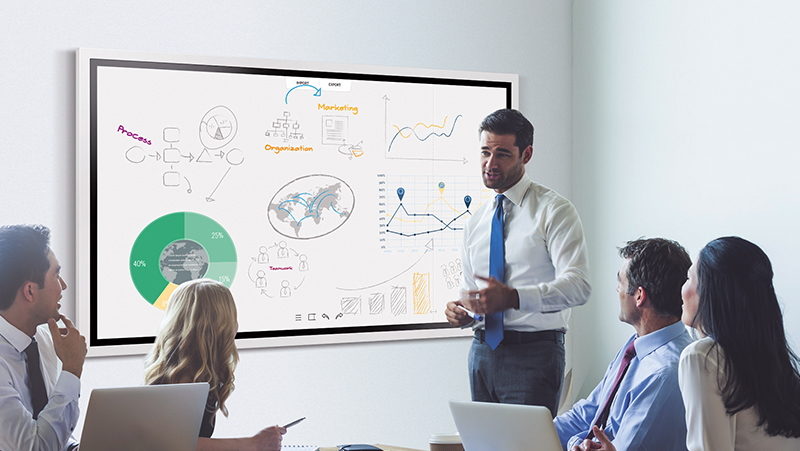
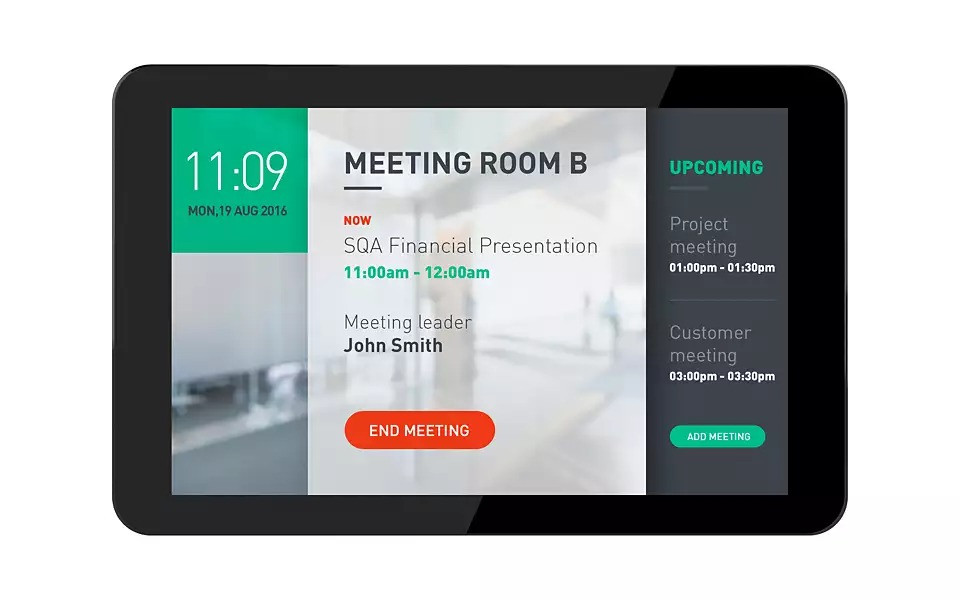
Interactive touch displays: working in the classroom and meeting room
Touch displays are screens that are equipped with a touch-sensitive surface for convenient operation of the applications displayed on the screen. The advantage of such displays is that they can be operated solely by pointing a finger (or using a stylus).
Furthermore, touch displays are often additionally equipped with advanced touch user interfaces, so that their operation by several users at the same time becomes child's play. There are several touch technologies that can be used in touch displays. In the professional large format display sector, these are mainly IR technology and capacitive touch technology.
Capacitive touch displays are generally better and more precise to control than IR displays. However, they are also more expensive and not yet as widespread. Touch displays are interesting and practical for both education and business. In both, they open up the space for better collaboration and thus for faster knowledge transfer. The best example of this is the Samsung Flip.
Videowall displays: The best eye-catcher
Videowall displays are the best eye-catcher. That is why they are preferred for digital signage. Here, several displays are combined to form a larger display area that can be filled with any content: Graphics, videos or animations. It is not uncommon for the videowall displays to have integrated signage players, features for convenient content management and various other functions for individual adaptation on site.
Tip:
Of course, you can also get a 360° display service from us: We will take care of the complete planning and installation of one or more displays for you!
Screen diagonal: What display sizes are available?
The screen diagonal tells you how big a display is. This is usually given in inches or, more rarely, in centimetres. The screen diagonal of the smaller displays starts at 10 inches, the larger ones at around 55 inches. Depending on where and for what you want to use a display, you can decide on a suitable display size.
Displays under 55 inches are perfect for use in almost any room, from a small reception to a meeting room or office. Displays with diagonals over 55 inches are more suitable for larger rooms, such as conference rooms, classrooms, lecture halls or larger reception areas in hotels. Displays with large diagonals are also preferable to smaller ones for digital signage at POS.
Displays with screen diagonals of less than 32 inches are unusual. These are usually found in the form of information stand display solutions in pillars or display housings for landscape or portrait mounting. Information stand displays are excellently suited as media for customer, employee and patient communication.
Typical screen diagonals for displays
| Screen diagonal in inches | Screen diagonal in centimetres |
| 32” | 81 cm |
| 42” | 107 cm |
| 55” | 140 cm |
| 65” | 165 cm |
| 75” | 191 cm |
| 85” | 216 cm |
All displays by size
Panel type for displays: Which is the best?
There are different types of panels used in displays, but LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) panels with IPS technology have become the most popular. Compared to TN panels, which are more commonly used in monitors, IPS technology is characterised by high contrast, colour fidelity and, above all, very good viewing angle stability.
Displays with OLED technology also conjure up a very high-contrast image. Here, the image is generated with the help of organic light-emitting diodes. The picture quality of these displays is outstanding! In addition, the depth of the housing is very small thanks to OLED technology. Therefore, they can be integrated very stylishly in almost any room. However, they are currently only available as signage and presentation displays, but not as touch displays.
Display mounts: For easy display installation
Displays can be mounted in different ways. The most common types of mounting include, for example, mounting via a wall mount, on a display stand or via a ceiling mount.