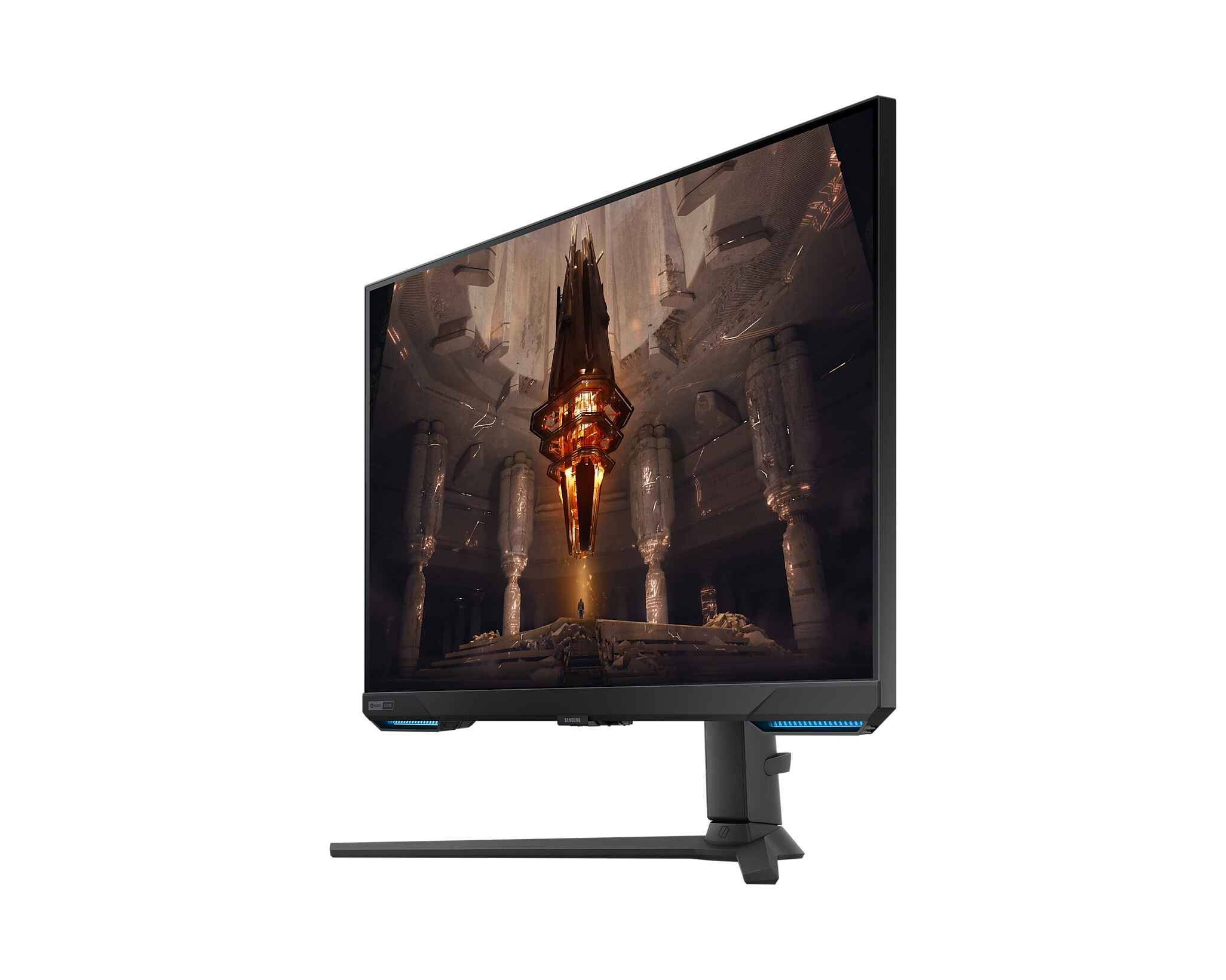
Monitors
Our visunext product experts will be happy to help you!
What is important when buying a PC monitor?
This depends very much on what you are looking for in a monitor. For example, do you want to buy a monitor that displays PC games in high resolution and has a good response time? Or, on the other hand, do you need several PC monitors for your office space for office applications? We explain what you should look for before buying a monitor.
Screen size: How many inches?
The screen diagonal determines the size of your monitor. It is given in inches ("). The following applies: The larger the inch value, the larger the screen area of the monitor.
Monitors with screen diagonals of 24″ to 27″ are popular. Converted into centimetres, this corresponds to screen diagonals of 60 cm and 68.5 cm. Screens of this size are universal: for most applications on the home computer or in business, these screen diagonals are perfectly adequate.
However, if you work with several programmes and want to have as many programme windows and widgets as possible clearly in view at the same time, we recommend larger screen diagonals of over 27″, for example 32″ (82 cm). With a PC monitor with a large screen diagonal, you can also keep an overview when editing videos or pictures.
The most popular screen diagonals for monitors
Our tip:
The larger the screen, the further away you should sit. An ideal viewing distance for a 24″ monitor is about one metre.
Monitor Panel Type: TN, VA, IPS
The type of panel is probably one of the most important selection criteria when looking for a suitable PC monitor. This is because it has a direct influence on the image display and ultimately also on whether a monitor is suitable for the intended use.
To avoid confusion: TFT and LCD are not panel types, but display technologies. They are used in almost all monitors. LED is a backlighting technology that is also used in all monitors except OLED screens.
However, a TFT LCD screen with LED backlighting can use one of three panel types: TN (Twisted Nematic), VA (Vertical Alignment) or IPS (In-Plane Switching).
The difference between these panel types is based on the orientation of the liquid crystals in an LCD panel. The respective different orientations simultaneously influence several properties of a monitor: some negatively, others positively.
Strengths and weaknesses of TN, VA and IPS
| Feature | TN | VA | IPS |
| Contrast | low to high | very high | high |
| Colour accuracy | low | very high | high |
| Viewing-angle stability | acceptable to good | very good | very high |
| Power consumption | low | moderate | high |
| Response time | very fast | slow | low to fast |
Monitor panel types and their applications
Screen resolution and format: From Full HD to 4K
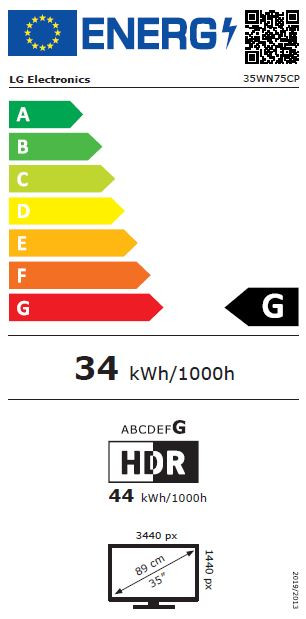
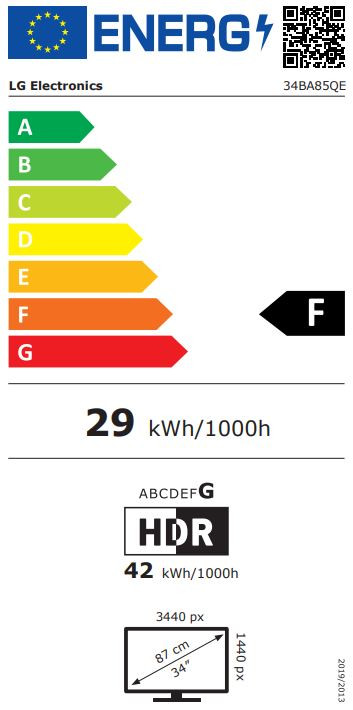
The screen resolution of a PC monitor is closely linked to its aspect ratio. For example, a Full HD monitor (1920 x 1080) has an aspect ratio of 16:9, a 4K-monitor (4096 x 2160) and a WQHD-monitor (2560 x 1440) likewise. A monitor with a resolution of 2560 x 1600 (WQXGA), on the other hand, has a slightly higher aspect ratio of 16:10.
This has to do with the fact that the format of a monitor is adapted to its native, i.e. optimal, resolution. Put more simply: the ratio of picture to frame must be right. Because in this way the proportions and the quality of the image are preserved.
Popular screen resolutions and their format
| Resolution | Aspect ratio |
| 1920 x 1080 Full HD | 16:9 |
| 1920 x 1200 WUXGA | 16:10 |
| 3840 x 2160 UHD | 16:9 |
| 4096 x 2160 4K | 16:9 |
| 2560 x 1600 WQXGA | 16:10 |
Of course, you can also play a higher resolution than the native one on any monitor, provided your graphics card supports this setting. However, we do not recommend this. A higher resolution on a screen that is not designed for it can, under certain circumstances, result in the font and symbols on the desktop, for example, appearing too small and possibly blurred. This tires the eyes and often leads to headaches.
In addition to the formats mentioned above, we also have monitors in special formats in our range, for example the 21:9 format. Special formats offer a larger work surface: large tables, several tools and application windows can now be clearly arranged on a single screen. A practical alternative to the two-screen solution.
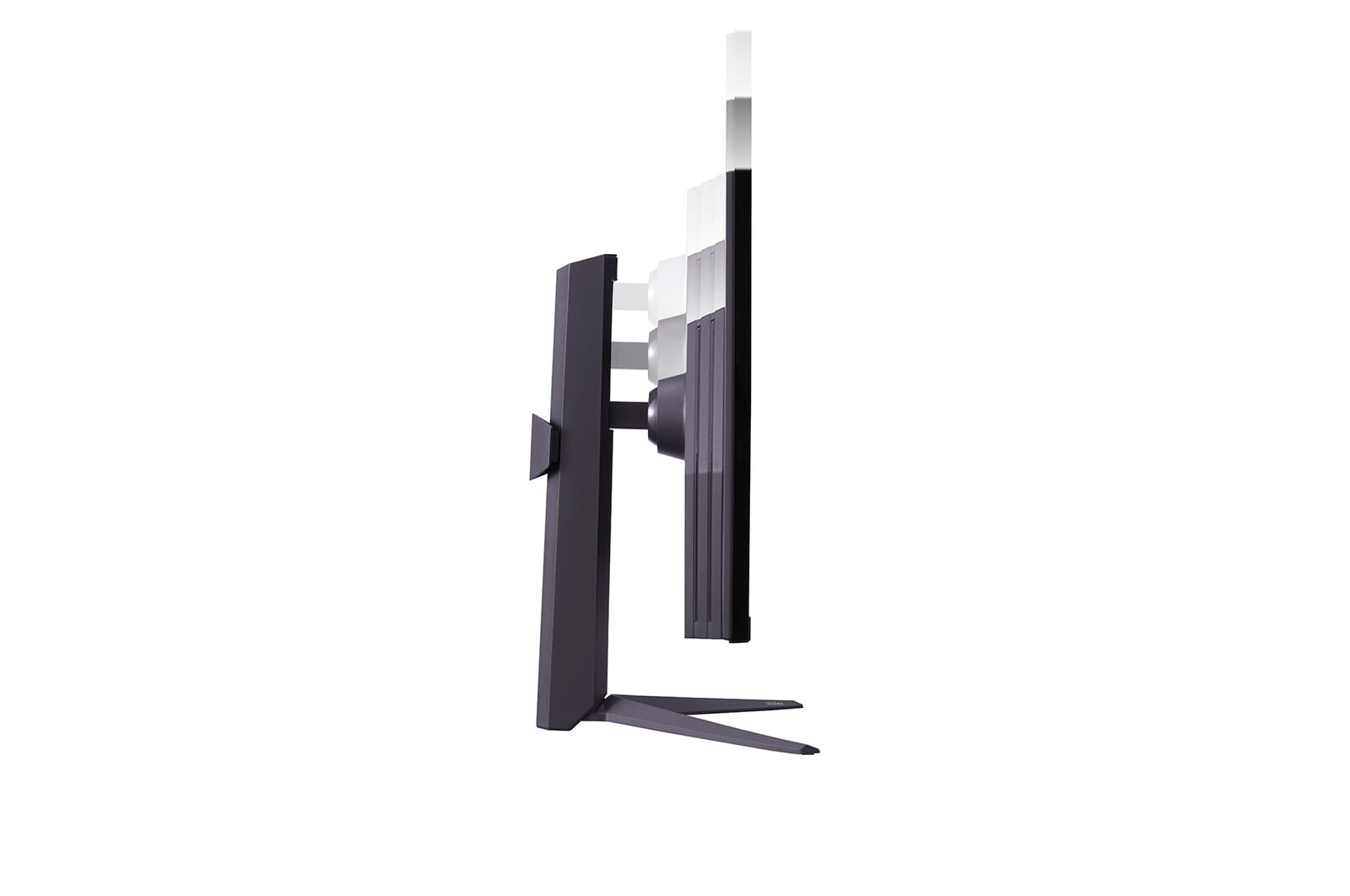
Ergonomics: Comfortable and gentle on the body
The term ergonomics is mainly known in connection with an optimal and, at the same time, a health- and body-friendly furnishing of the workplace. However, ergonomic design also plays a major role outside the office.
Ergonomic design is especially important for monitors: a height-adjustable and tiltable monitor can be ideally adjusted to your eye level. This ensures a healthy posture and prevents neck and back pain. With a well-aligned monitor, you also avoid eyestrain.
A height-adjustable monitor is a wonderful addition to your notebook. On the one hand, you have the possibility to set up a PC screen in your office or home in a suitable way, and on the other hand, you remain mobile with your notebook.

Our tipp:
Ensure a straight posture when working at the computer. A height-adjustable monitor can only compensate for a limited height difference. Therefore, we recommend that you also adjust the height of your desk and office chair accordingly.
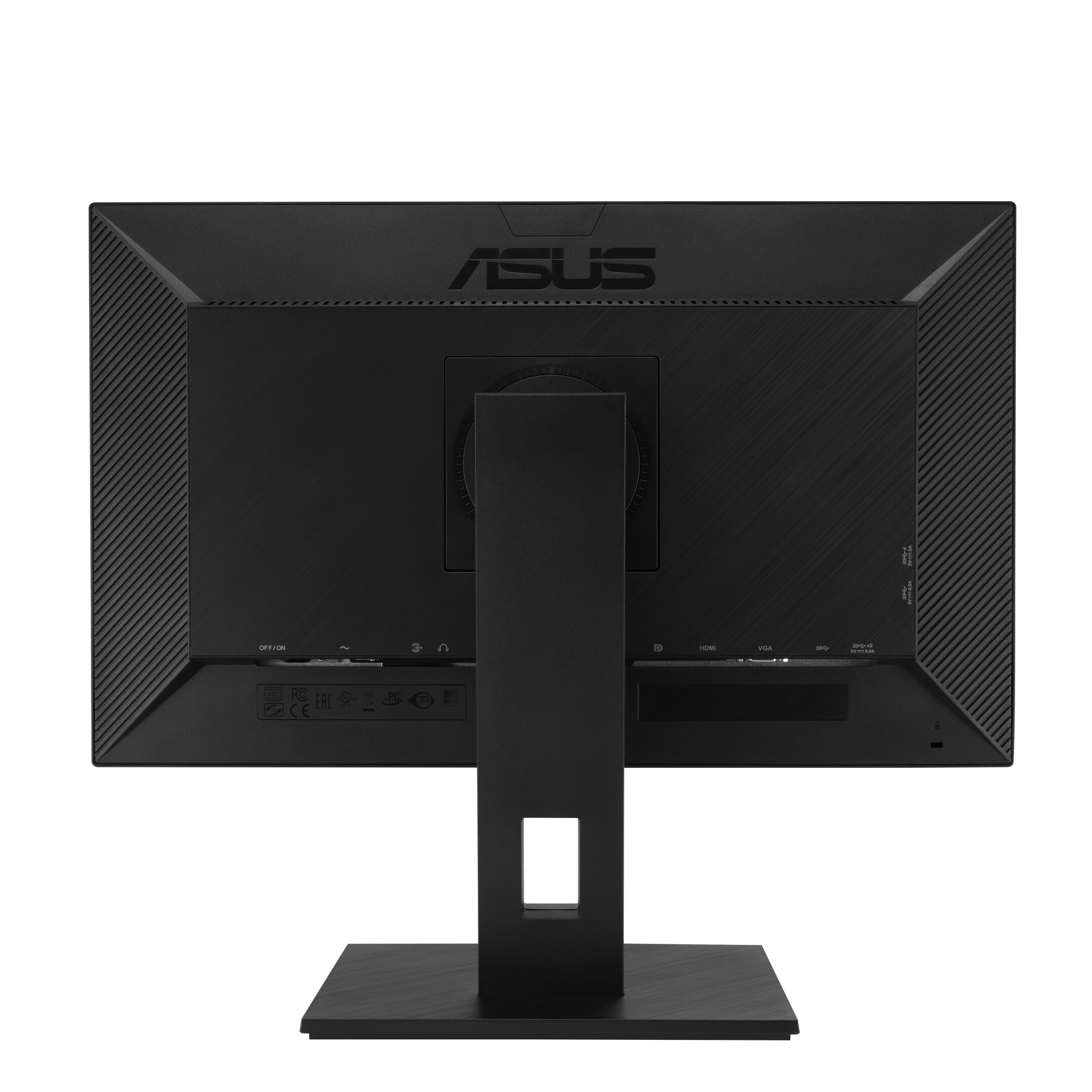
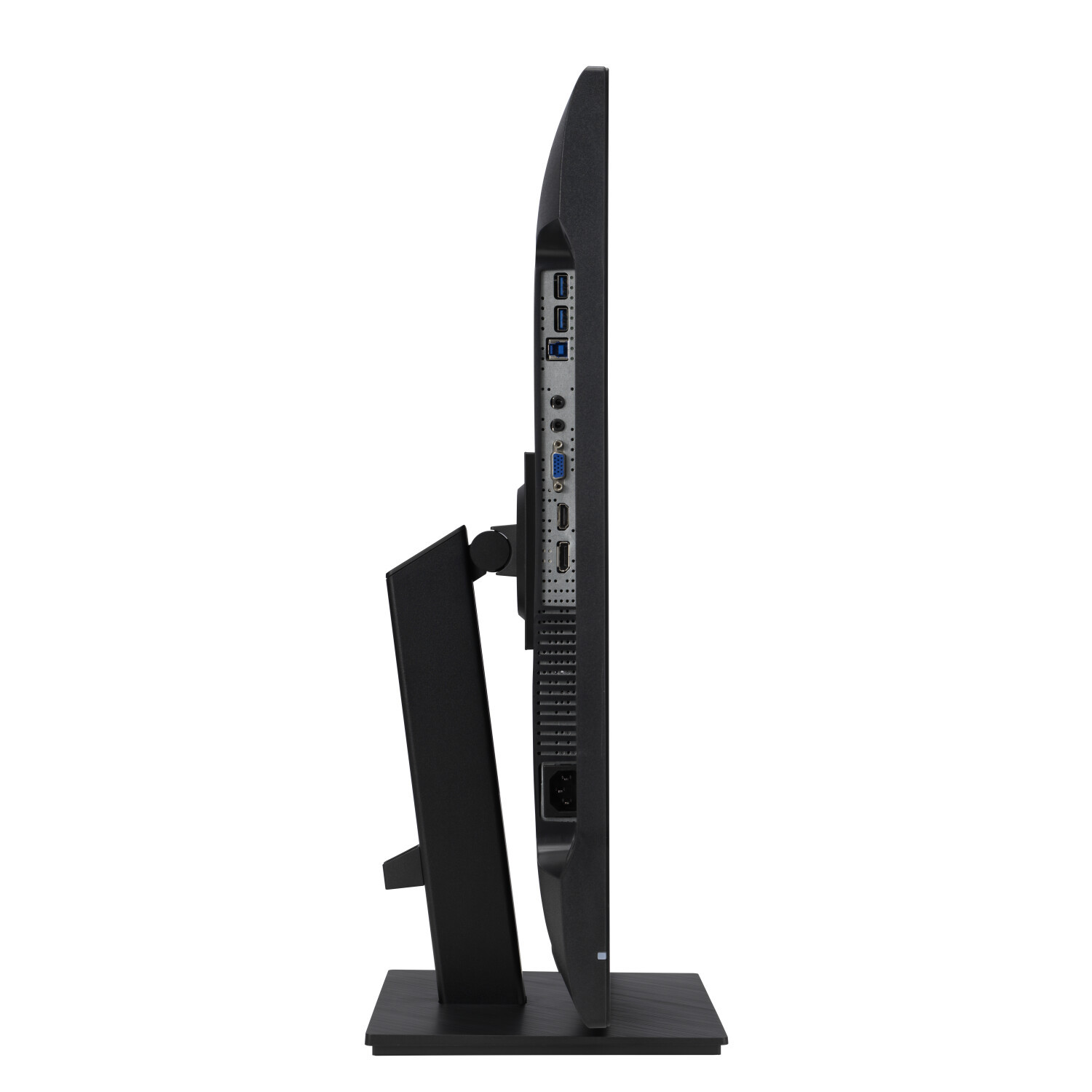
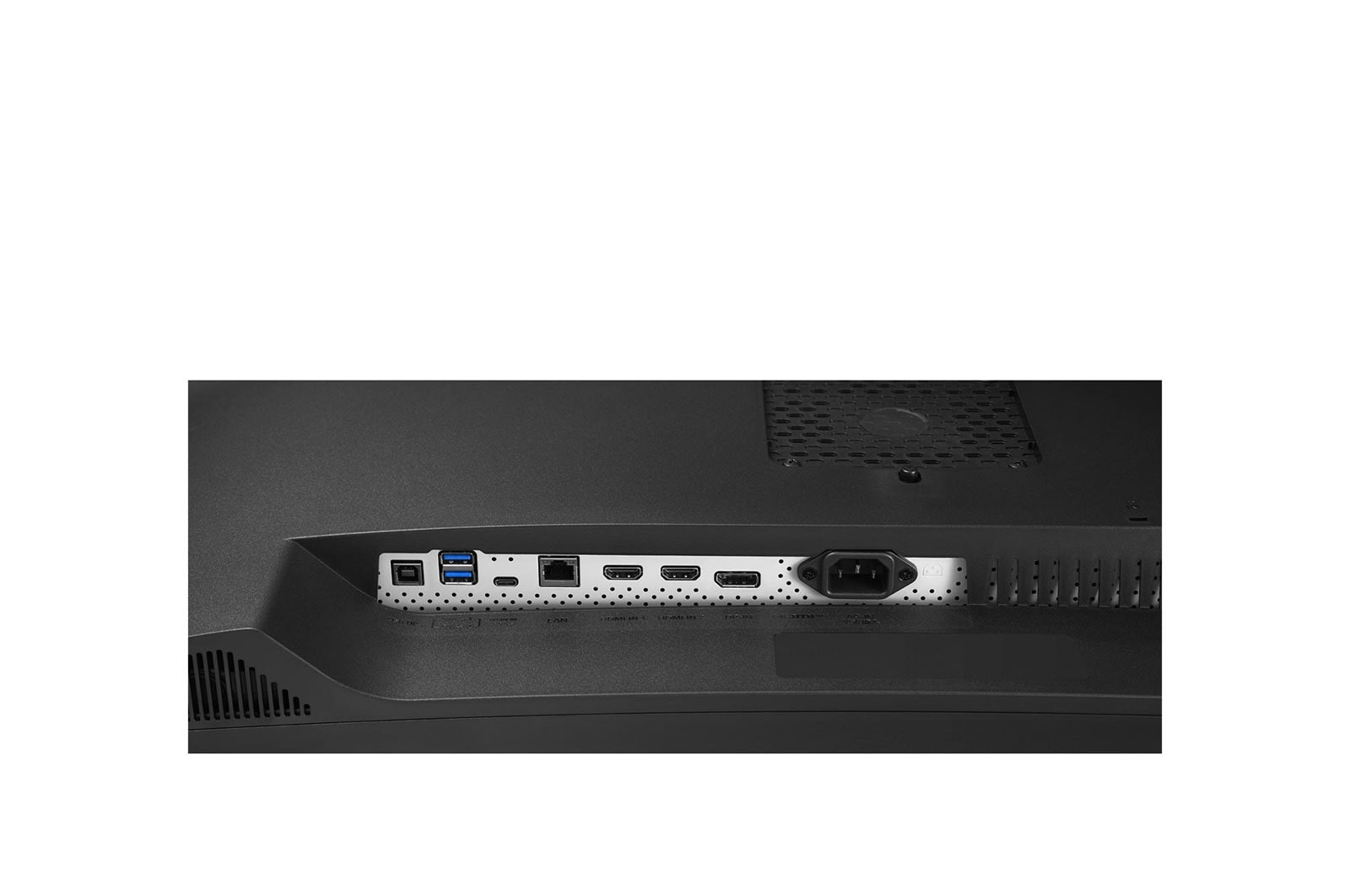
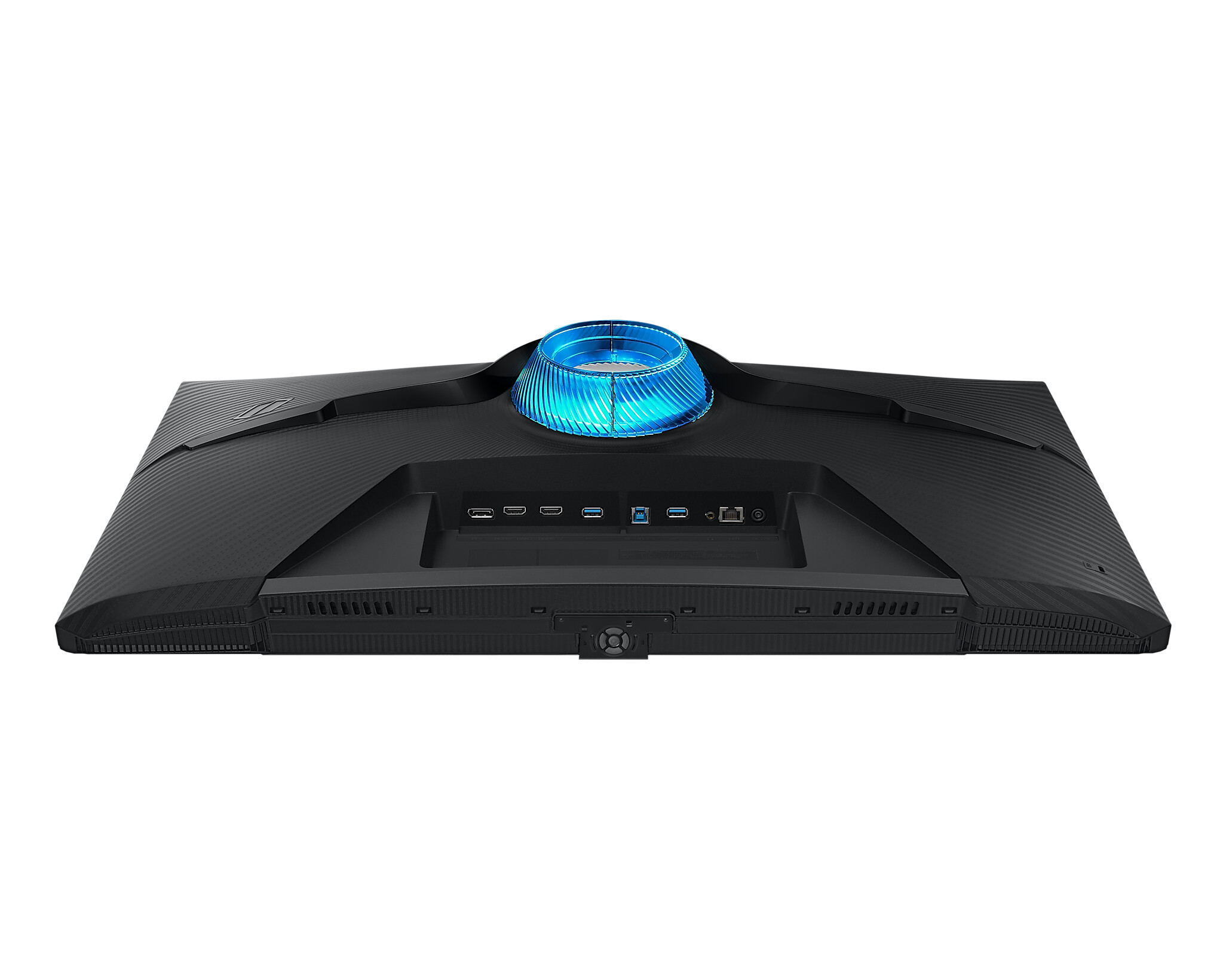
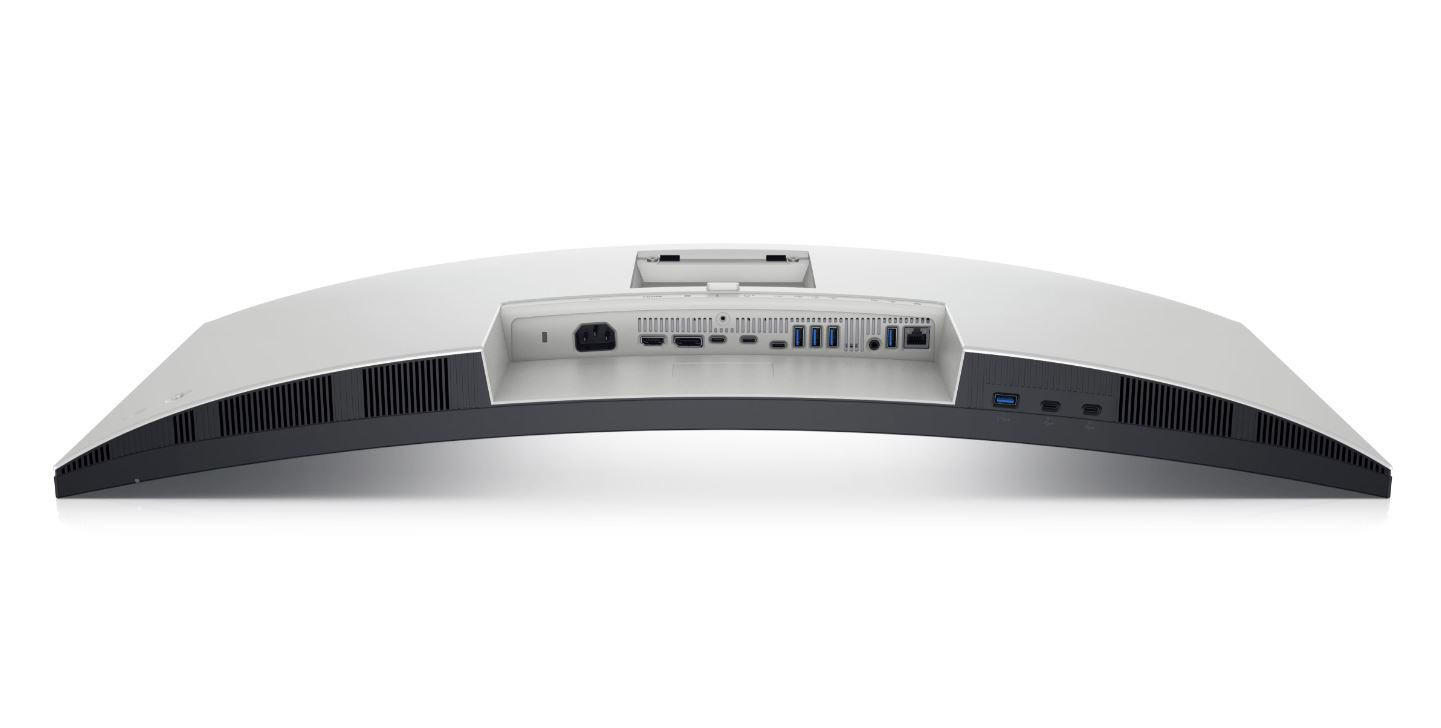
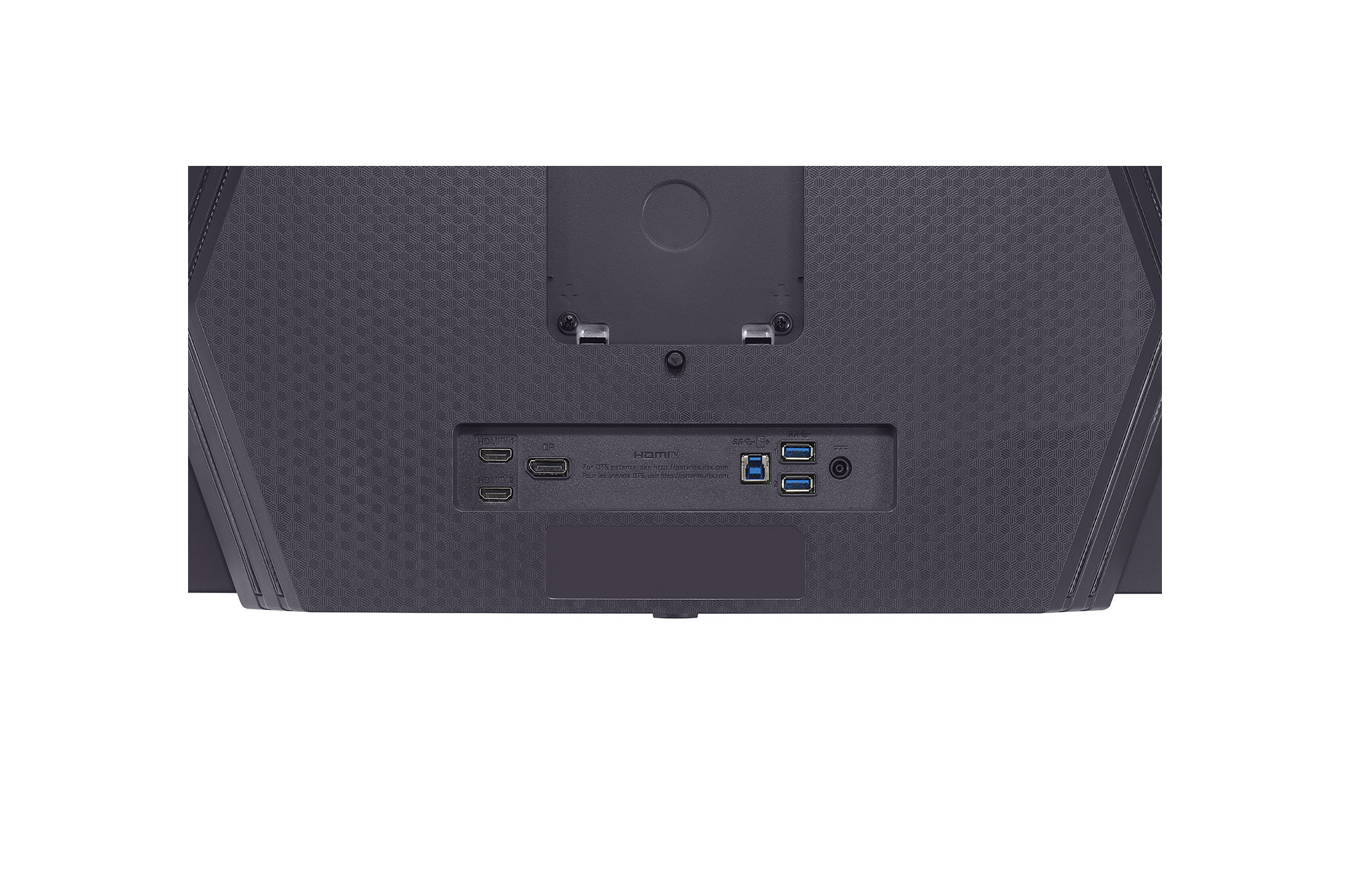
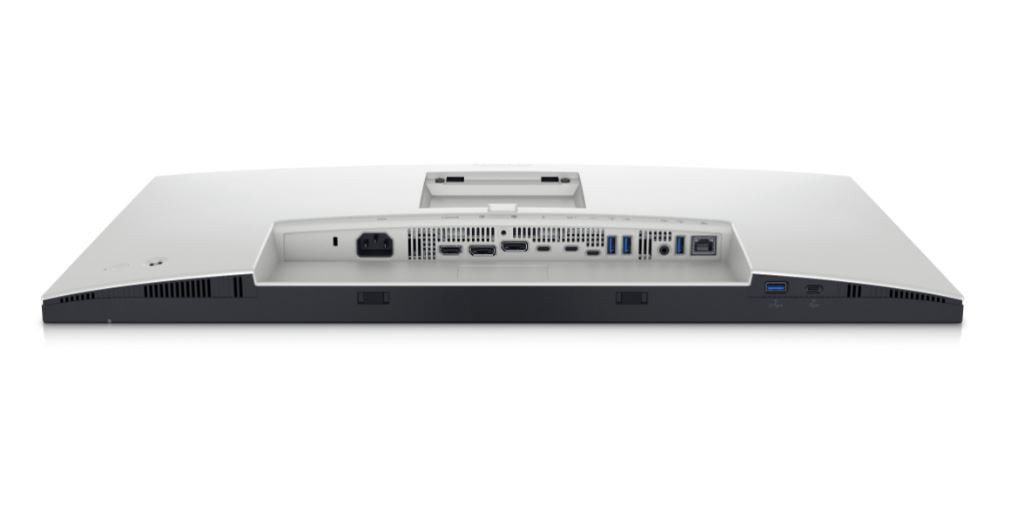
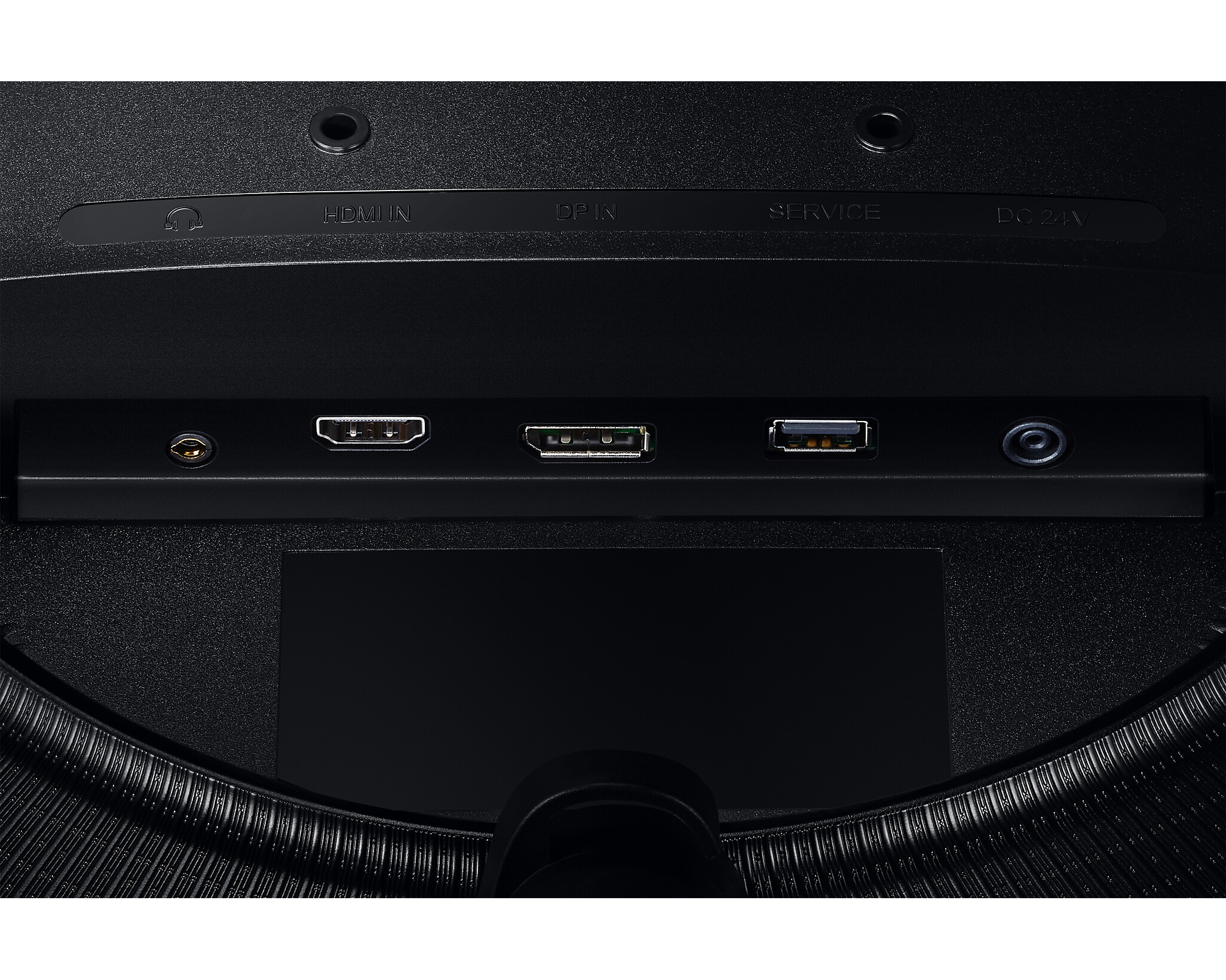
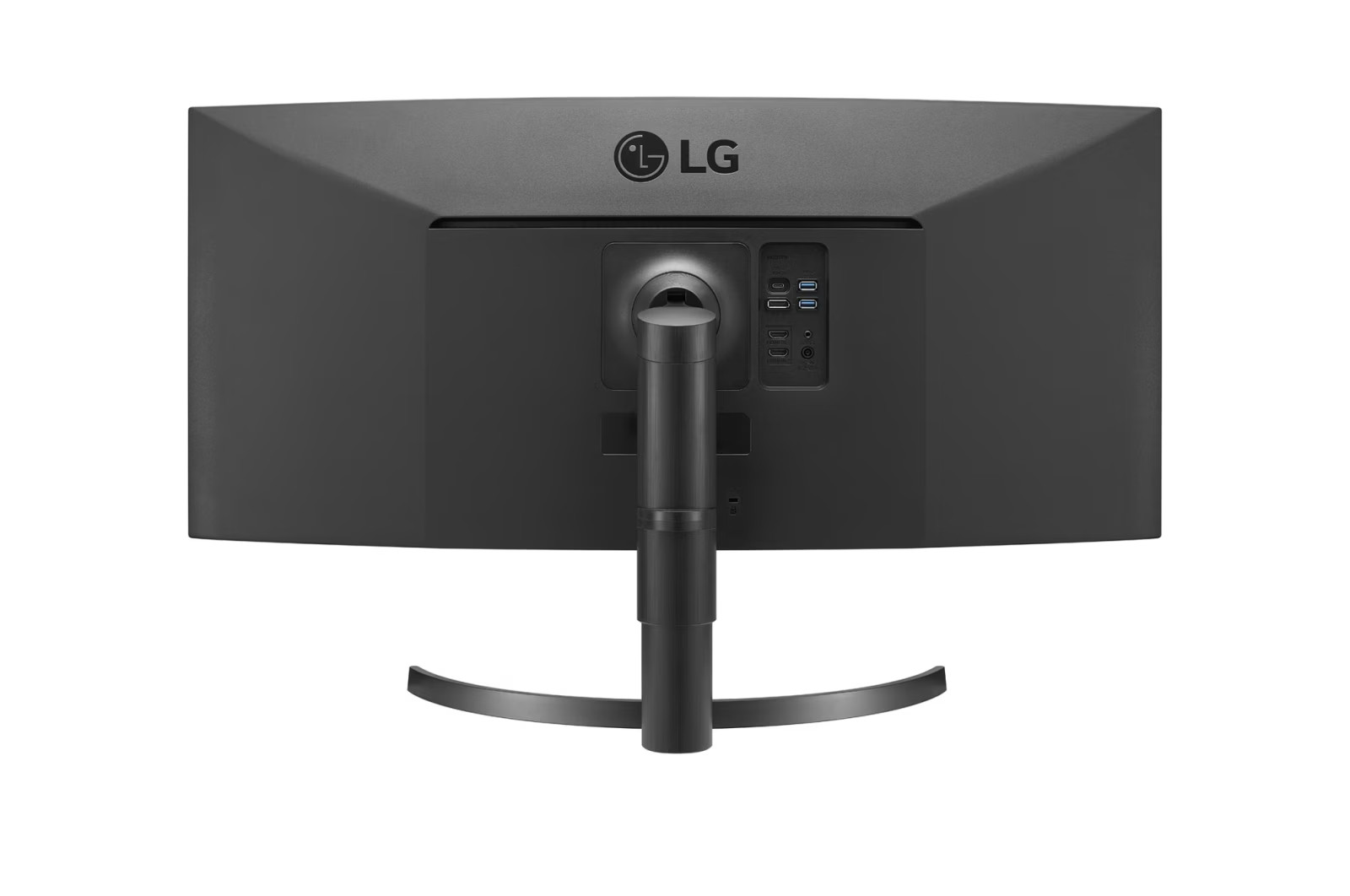
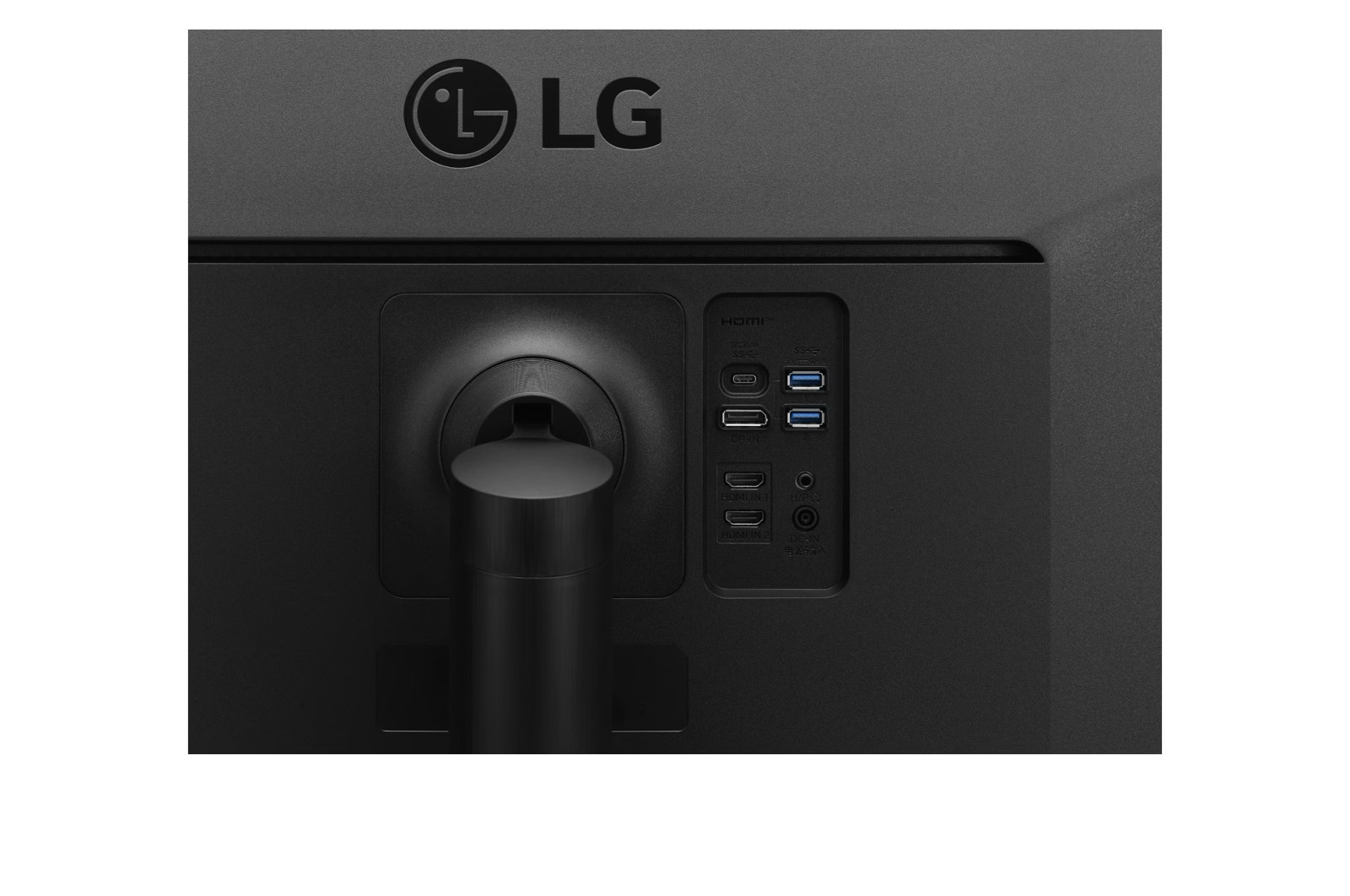
Connections: DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort and USB-C
A modern monitor usually has several connections. The most common is HDMI (High-Definition Media Interface), followed by DVI (Digital Visual Interface) and DisplayPort. Depending on the manufacturer, a monitor can also be equipped with several connections of one type, for example with two HDMI inputs.
Technology for gamers: G-Sync and FreeSync
Monitors with G-Sync or FreeSync are the first choice for gamers: these technologies synchronise the refresh rate of a monitor with the frame rate of a PC game. In this way, they eliminate annoying tearing (tearing of the image) and annoying jerkiness in the image. Nothing stands in the way of smooth gaming.