


































£1,312.73*
- Resolution 5120 x 1440
- Diagonal 49"
- Panel type IPS
- Refresh Rate 144Hz


Product information
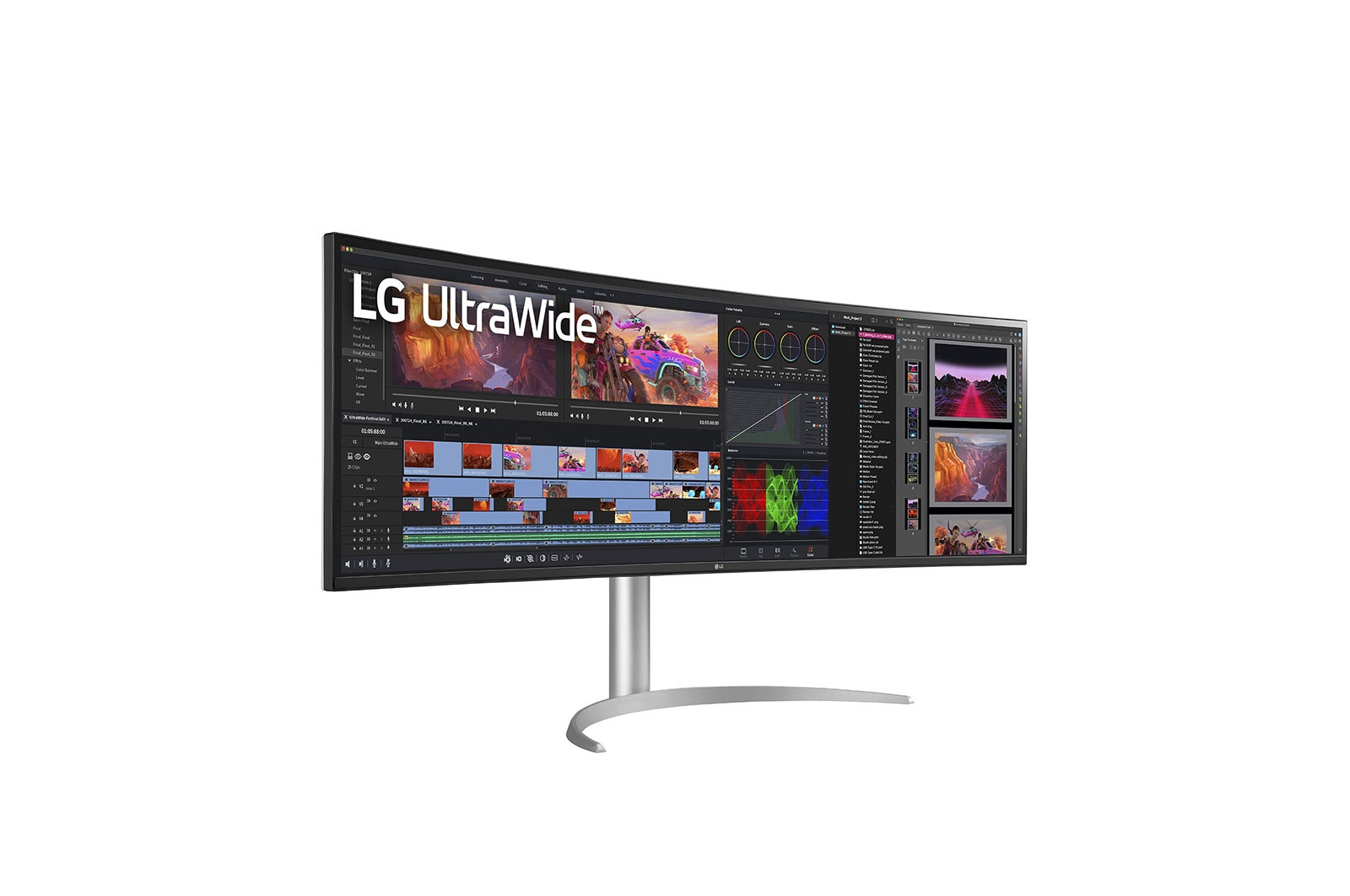
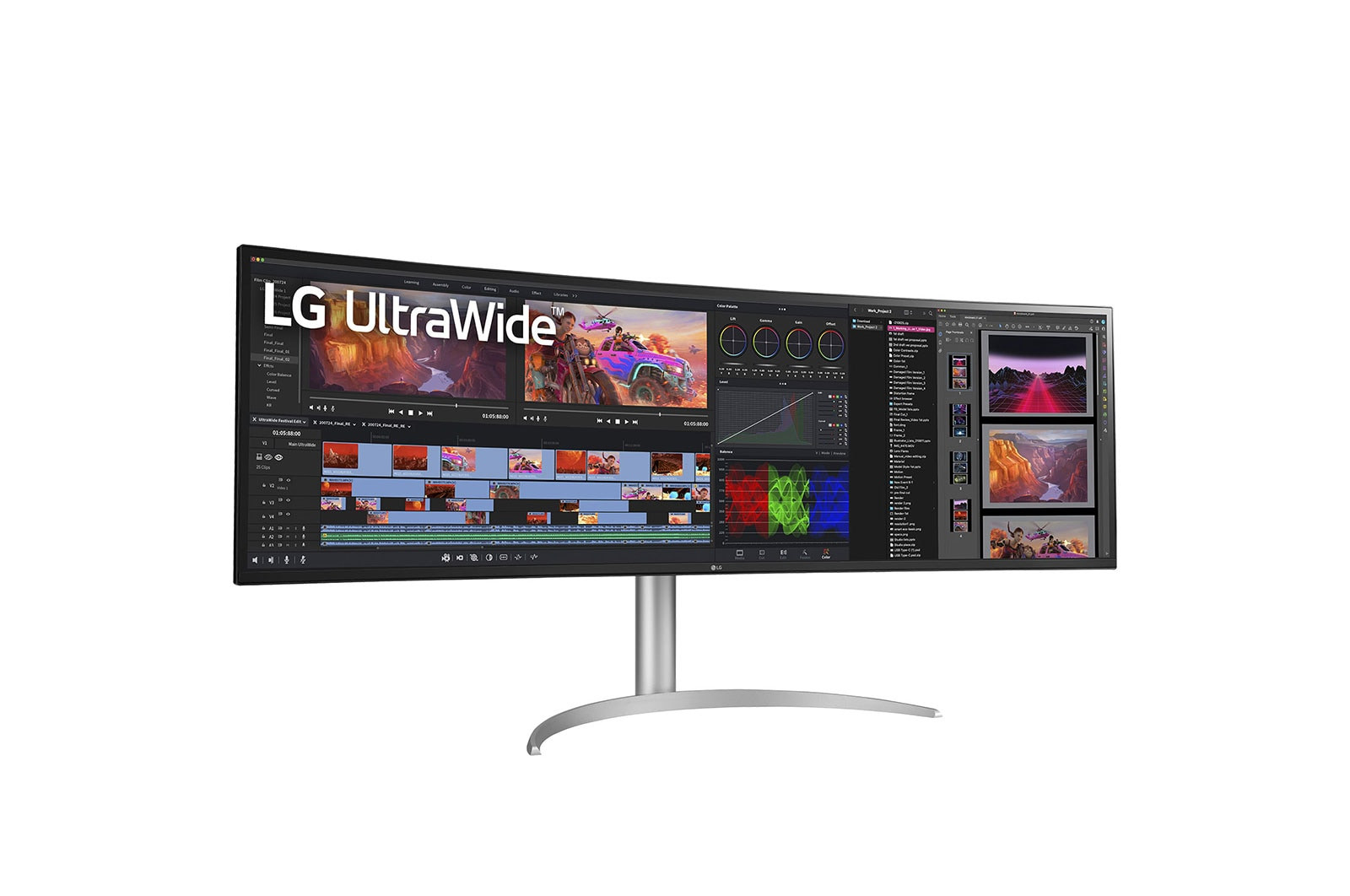
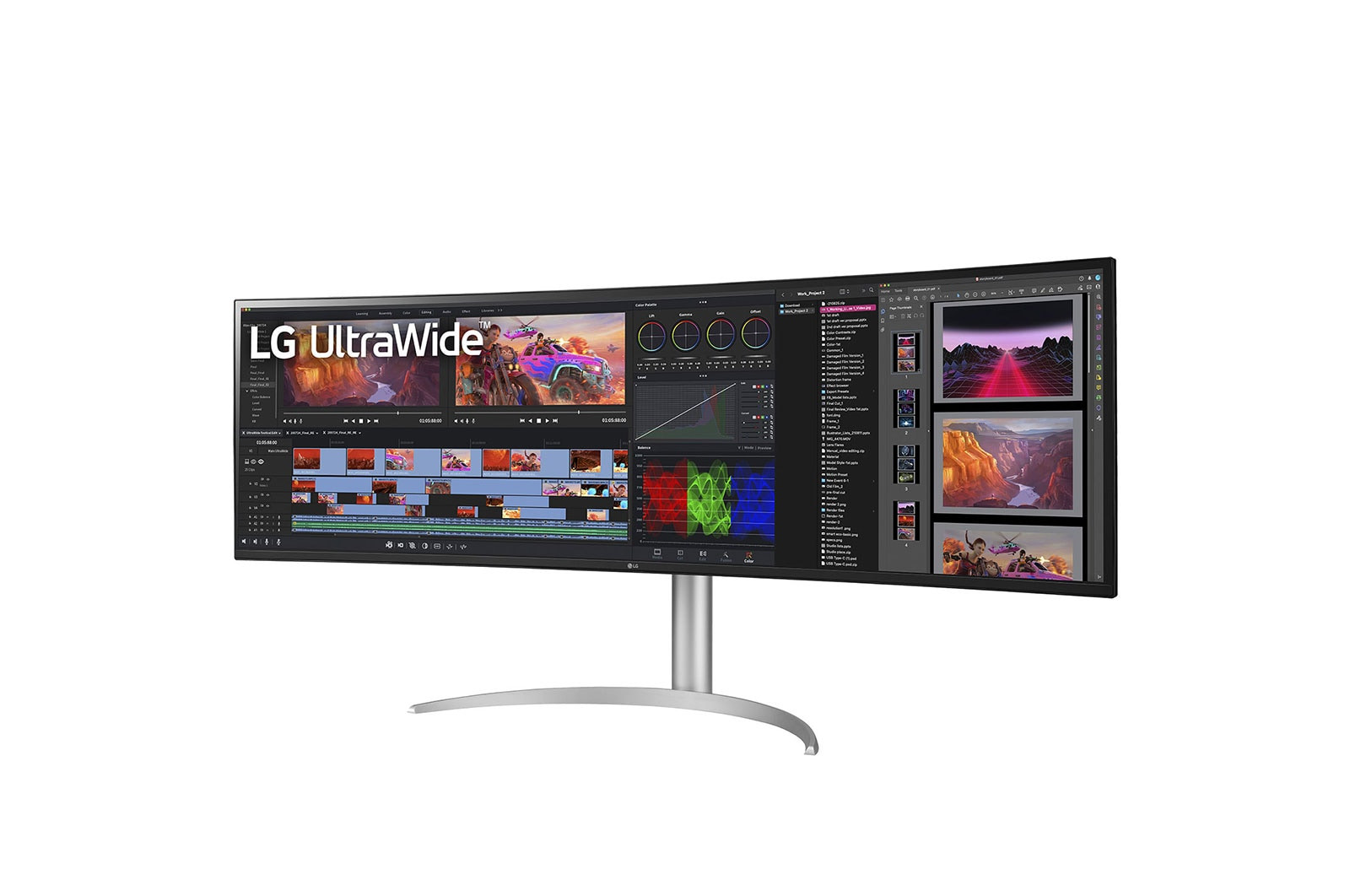
The LG 49BQ95C-W UltraWide™ monitor combines impressive size with state-of-the-art technology for professional users, creatives and gamers. With its 32:9 format and dual QHD resolution of 5,120 x 1,440, it offers a huge work surface on which multitasking is possible without compromise. In addition, Nano IPS, HDR10 and a variety of gaming features ensure a breathtaking viewing experience.
The most important technical data at a glance:
- Screen diagonal: 49 inches
- Resolution: Dual QHD (5.120 x 1,440)
- Aspect ratio: 32:9
- Panel type: Nano IPS™
- Colour space: DCI-P3 98%
- HDR: VESA Display HDR™ 400
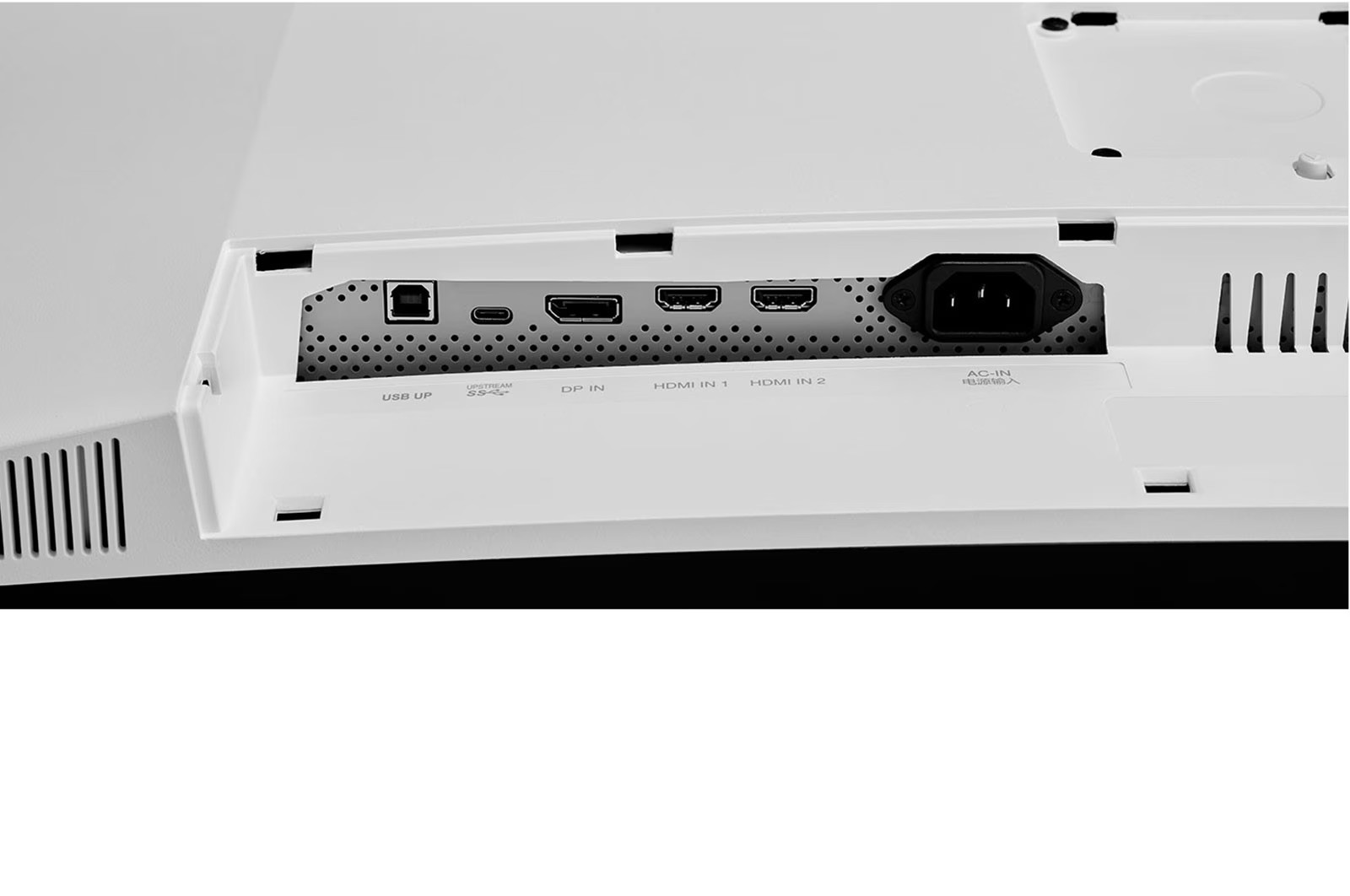
- Ports: USB Type-C™, HDMI, DisplayPort
- Ergonomics: Height-adjustable, tiltable, swivelling
- Gaming: 144 Hz, NVIDIA® G-SYNC® Compatible, AMD FreeSync™ Premium Pro
More space for multitasking - efficiency redefined
With its 32:9 format and dual QHD resolution, the LG 49BQ95C-W offers an enormous workspace that revolutionises multitasking. Instead of switching back and forth between windows, several applications can be displayed simultaneously on the screen. Ideal for creative professionals working on extensive projects such as video editing and audio production, but also for office tasks or participating in webinars with many participants.
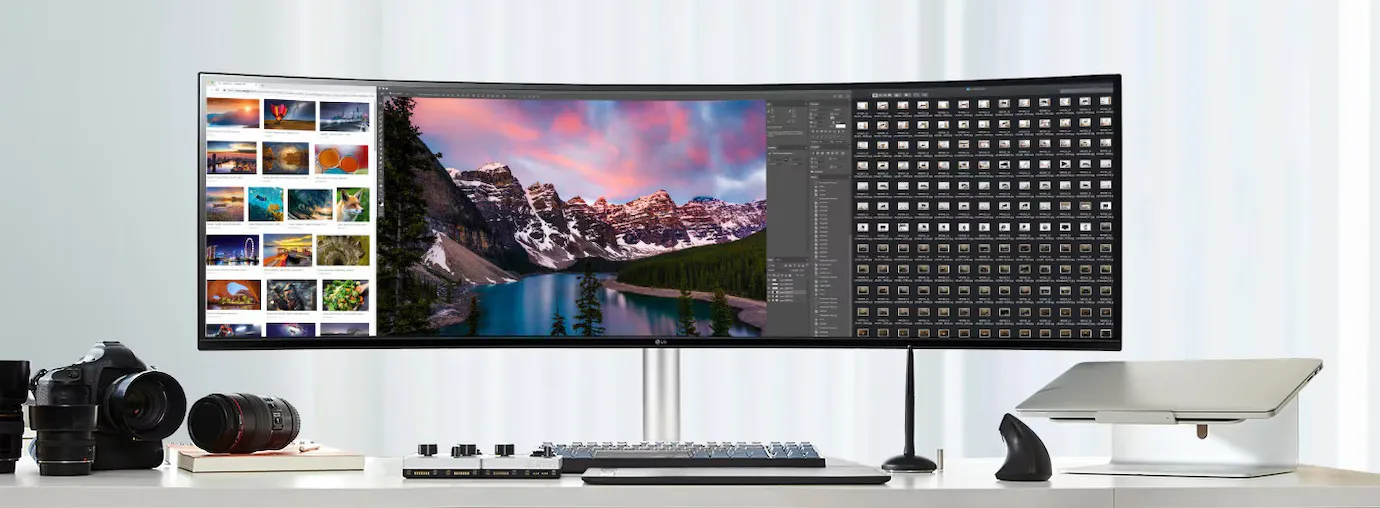
Nano IPS and HDR10 - Precise colours and vivid brightness
The Nano IPS™ display of the LG monitor covers 98% of the DCI-P3 colour space and thus offers highly precise colour reproduction. VESA Display HDR™ 400 supports vivid colours and detailed contrast, so that visual content is displayed in the highest quality. For creative applications in particular, colour accuracy is crucial for realising projects in the best possible quality.

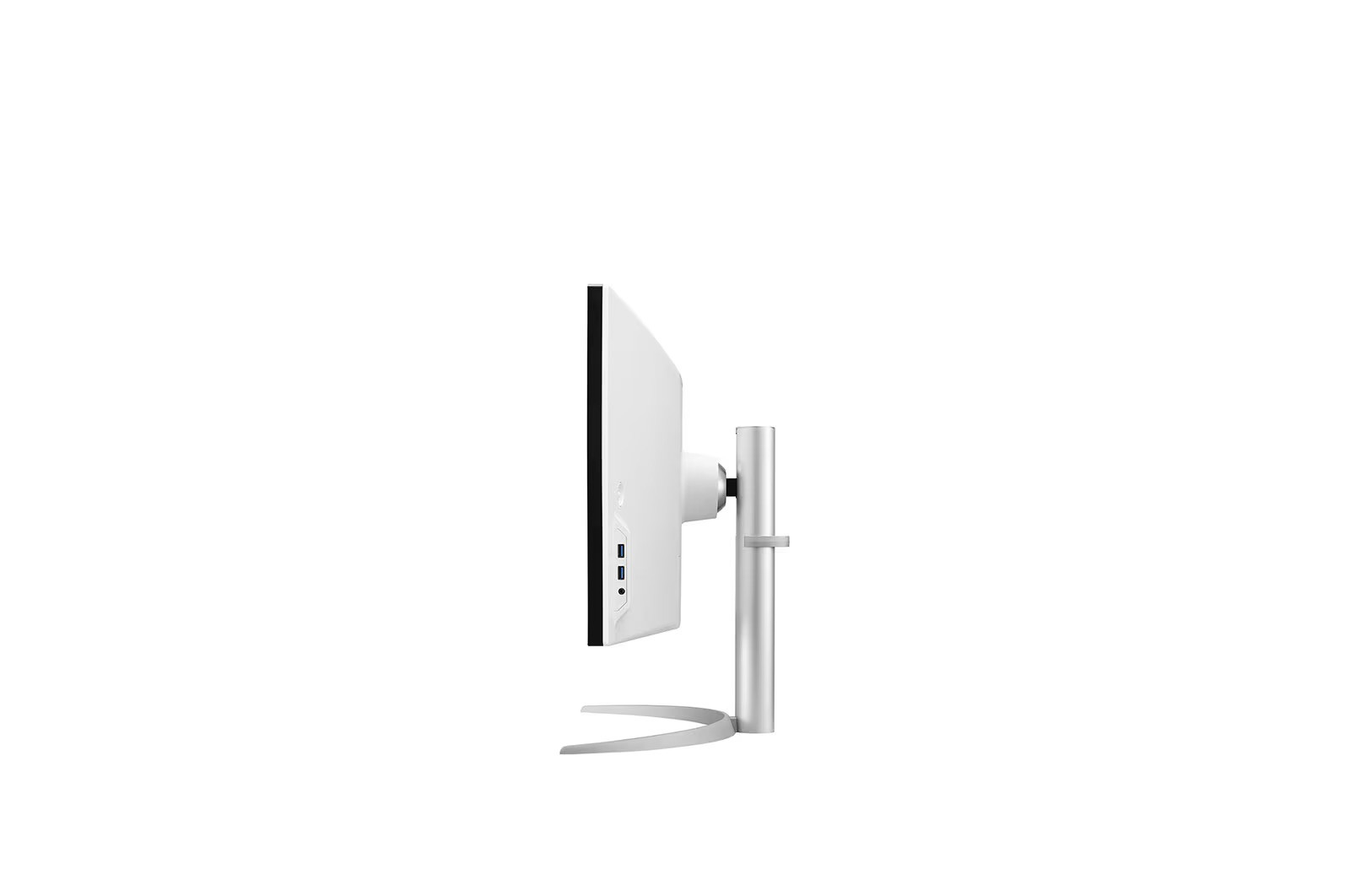
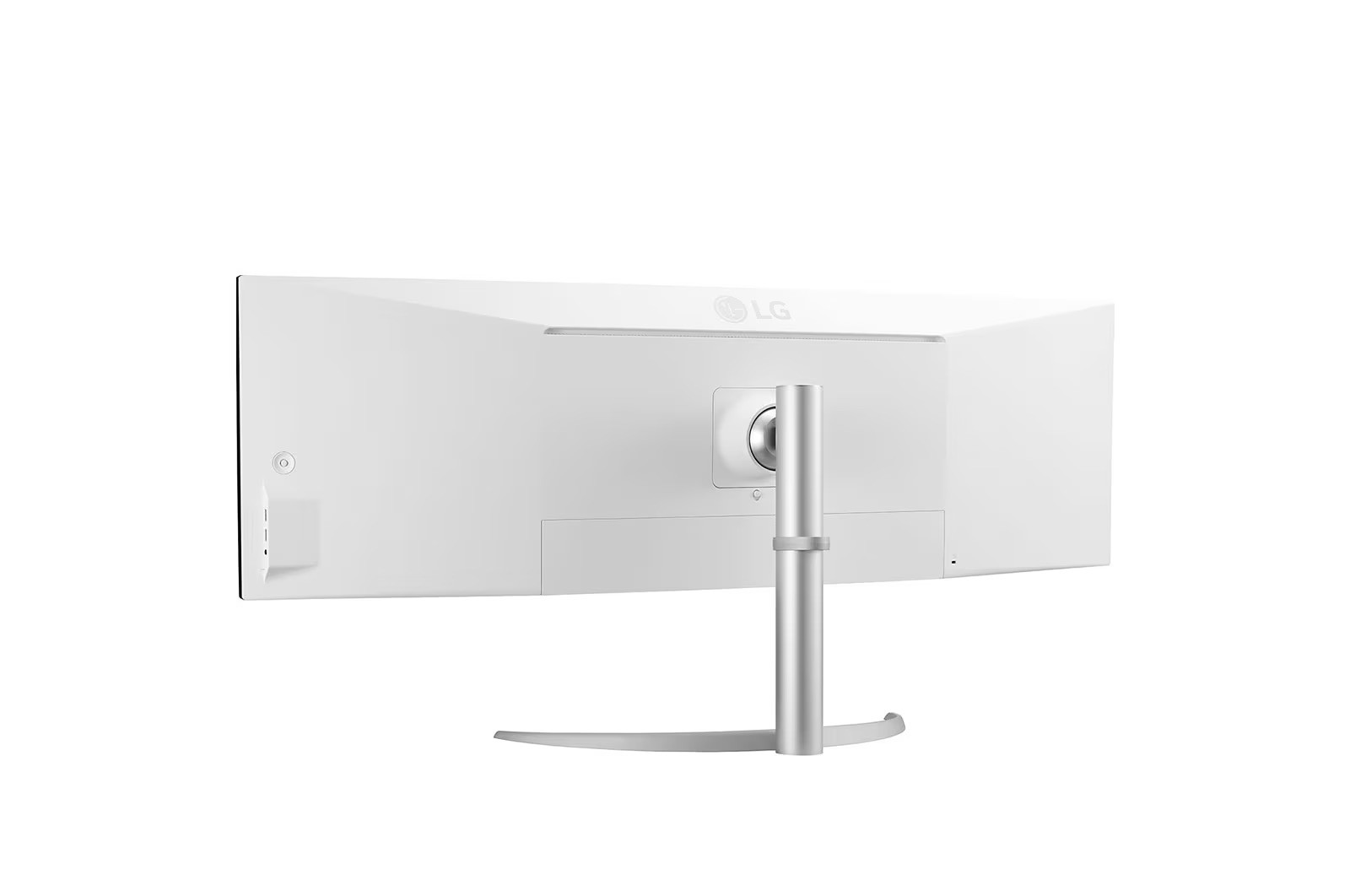
Ergonomic design - Flexible and comfortable
The LG 49BQ95C-W offers versatile ergonomic customisation options that increase working comfort. With height adjustment, tilt and swivel options, the monitor adapts perfectly to any working environment. The narrow frame on three sides and the ability to position the monitor flexibly guarantee effortless integration into any setup.
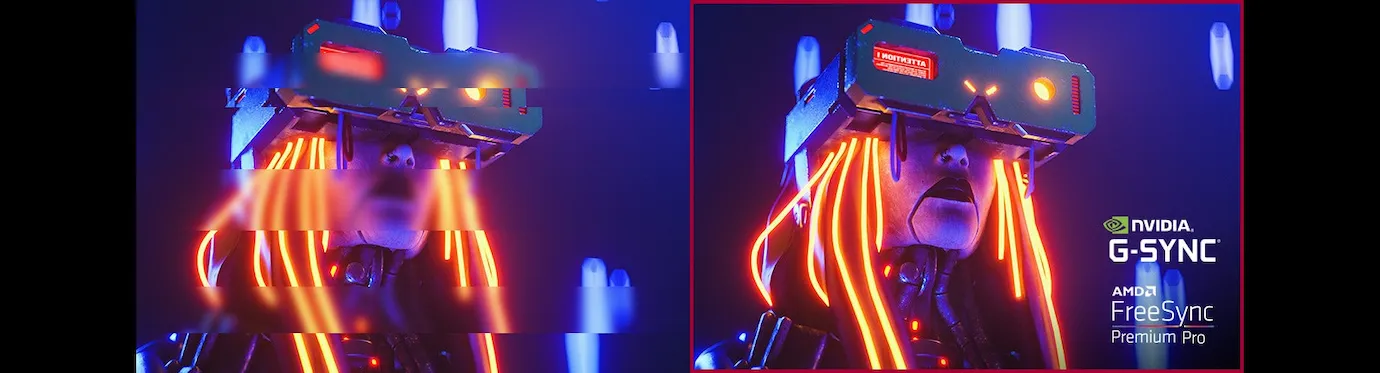
Gaming performance at the highest level - 144 Hz and FreeSync™
For gamers, the LG 49BQ95C-W is equipped with a refresh rate of 144 Hz and support for NVIDIA® G-SYNC® Compatible and AMD FreeSync™ Premium Pro . These technologies ensure fluid, smooth gameplay, even in fast and action-packed games. Features such as Dynamic Action Sync and Black Stabiliser allow gamers to react to enemies at lightning speed and stay in control even in dark scenes.
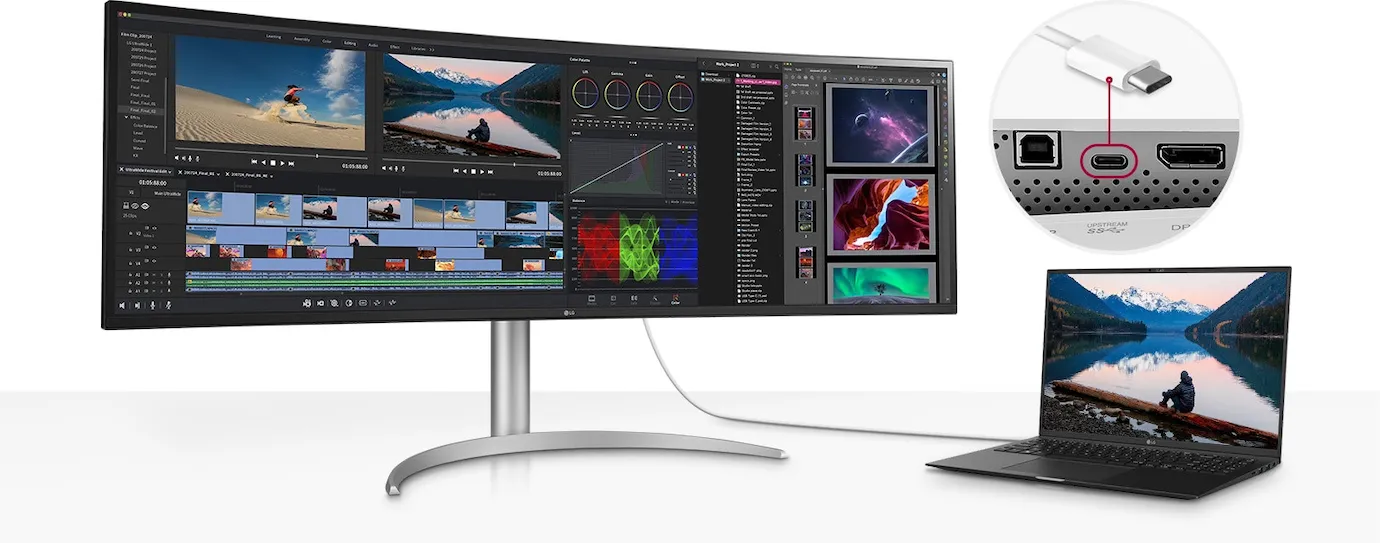
Connectivity and integrated sound - everything you need
The USB Type-C™ port not only enables fast data transfer, but also charging of connected devices with up to 90 W. In addition, the two integrated 10-watt speakers with MaxxAudio® provide clear and powerful sound that rounds off the immersive experience and eliminates the need for external speakers. Ideal for creative projects and entertainment alike.
The LG 49BQ95C-W is the ideal monitor for anyone looking for a large, powerful work and gaming surface. With first-class technologies and ergonomic design, it fulfils the highest demands in every application.
Technical data
| Name | LG 49BQ95C-W 49" IPS Monitor, 5120 x 1440, 144Hz, 5ms |
|---|---|
| Article number | 1000033178 |
| GTIN/EAN | 8806084665737 |
| Manufacturer SKU | 49BQ95C-W.AEU |
| EPREL ID | 1,589,478 , 1589478 |
| Model name | 49BQ95C-W |
| Brand | LG |
| Product Type | Monitor |
| Product Series | LG Business Series |
| Panel type | IPS |
| Resolution | 5120 x 1440 |
| Diagonal | 49" |
| Aspect Ratio | 32:9 |
| Viewing angle - Horizontal | 178° |
| Viewing angle - Vertical | 178° |
| Contrast Ratio | 1,000 :1 |
| Max. Brightness | 400 cd/m² |
| Response time | 5ms |
| Refresh Rate | 144Hz |
| Support - VESA | 100 x 100 |
| Inputs | 1x Displayport , 1x USB-A , 1x USB-C , 2x HDMI |
| Outputs | 1x 3,5mm Jack |
| Product width | 121.51 cm |
| Product height | 11.42 cm |
| Product depth | 36.57 cm |
| Weight | 14.7 kg |
| Colour | White |
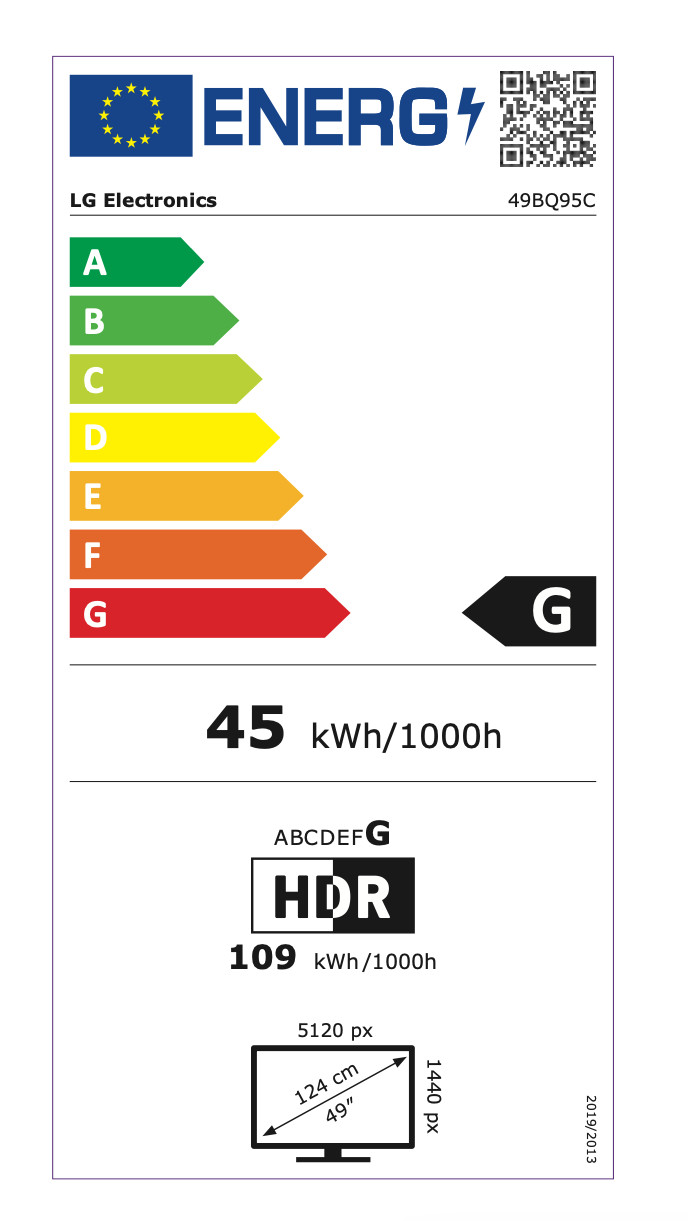
| EEK Spectrum | A to G |
| Energy efficency class | G |
| Condition | New |
| Warranty | 36 Month |
| Warranty type | Swap service Service and support information |
Product safety
| Person responsible for the EU |
|---|
| LG Electronics Deutschland GmbH |
| Alfred-Herrhausen-Allee 3-5 |
| 65760 Eschborn |
| Germany |
| info@lge.de |



