







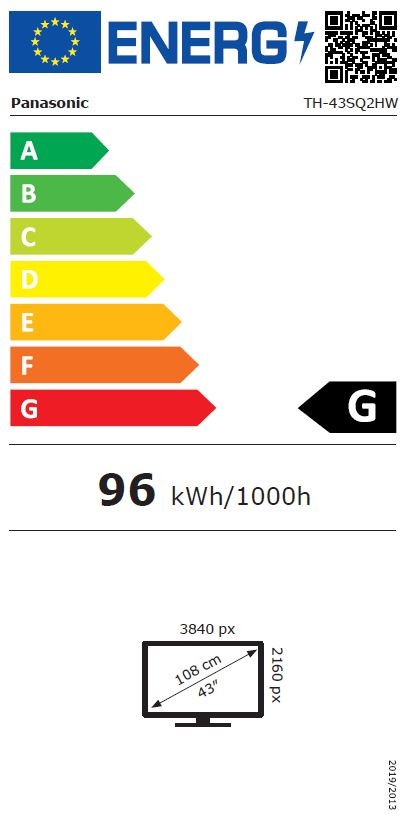
£1,529.56*
- Resolution 3840 x 2160 4K UHD
- Max. Brightness 700 cd/m²
- Panel type VA
- Contrast Ratio 1,200 :1


Product information
Breathtaking 4K quality from Panasonic: brilliance down to the smallest detail
With a high resolution of around 8,290,000 pixels - four times that of a Full HD display - extremely detailed images are delivered. This dynamic large-screen display archives lifelike, finely nuanced images. The 4K display is an excellent choice for meeting rooms where images are often viewed up close and creates an impressive ambience in signage applications for commercial facilities. It is expected to attract considerable attention.

A clear display of images even in brightly lit places
The SQ2H series has a brightness of 700 cd/m² and therefore delivers significantly brighter images than a conventional 4K display.
Ultra-high-resolution 4K displays from the "SQ2H" series with a brightness of 700 cd/m² provide strong visibility even in bright conditions and deliver significantly brighter images than a conventional display.
Even next to a window, these displays can be used effectively to share information in a classroom or conference room and are well suited for in-store digital signage placed in well-lit areas.

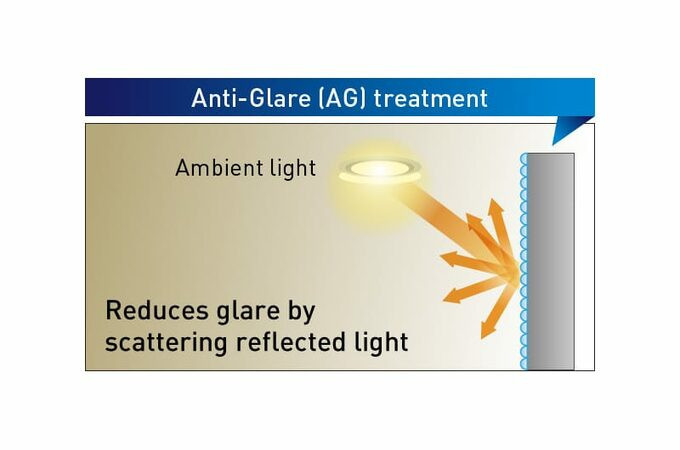
Best readable panel surface finish
The SQ2H series uses a panel with anti-glare (AG) processing, which utilises the concave/convex surface to diffuse the light from the sun and lighting equipment. As it suppresses external reflections to ensure better readability, it is ideal for use in conference rooms and lecture theatres.
High reliability enables continuous 24/7 operation
The SQ2H series is capable of continuous 24/7 operation. It offers reliable use in public spaces where many people gather, such as train stations, airports and shopping centres, as well as for installation in control rooms.
Customised installation for every application
Large selection of 98- to 43-inch models to suit your space, from small corners such as a meeting room to the main display in a conference room. It can also be installed tilted forward at an angle of up to 20 degrees to ensure good readability when mounted in a high position.

Support of the new Intel® SDM slot standard
The SQ2H series is equipped with the Intel® SDM specification slot standard, which supports 4K signals. In combination with the interface board, you can easily use a built-in PC and add various interfaces.
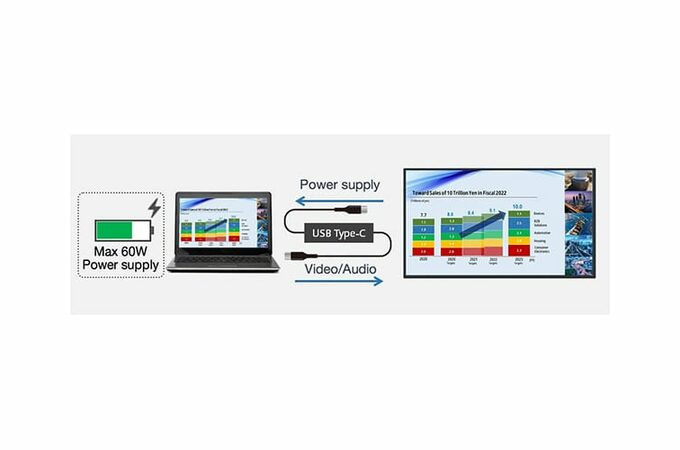
Numerous terminals allow connection to various devices
Equipped with HDMI inputs (x 3), PC-™ and USB Type-C video inputs. Depending on the operating environment, various video contents can be displayed by connecting external devices. When the SQ2H series is connected to a PC via USB Type-C, up to 60 W of power can be delivered to the PC.
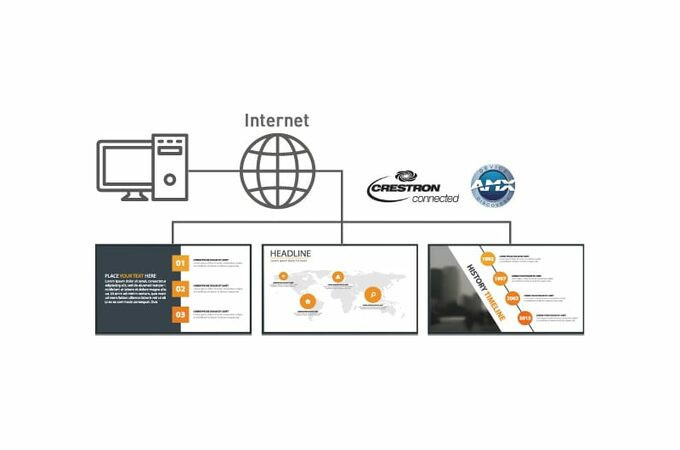
Supports LAN control connection
The SQ2H series can be controlled via LAN or serial. Simultaneous control and centralised management can be carried out via a network. It is also compatible with AMX, Crestron Connected™ and Crestron XiO Cloud™.
Screen transfer function that allows you to distribute images to displays in every classroom and conference room
Compatible with Screen Transfer version 2.3 software, which displays the PC screen on up to 64 displays via wired LAN.
Distribute headmaster or teacher presentations and in-house training status to multiple classrooms and conference rooms and confirm distribution status from one PC.
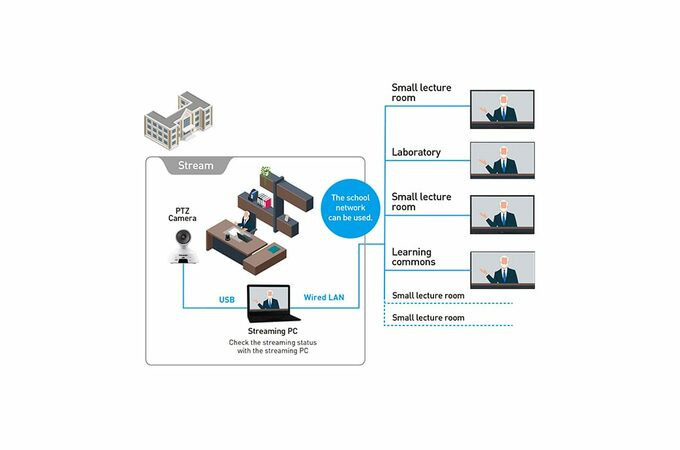
With the priority distribution function, you can distribute images in the wrong order or switch the device on automatically so that you can distribute messages in an emergency.
Enables you to write on the screen
The SQ2H series is equipped with a whiteboard function. By setting the USB receiver of the mouse on the display, you can write on the screen with the mouse and zoom in and out. This is useful for facilitating efficient meetings.

USB pass-through function to save time and effort when preparing for meetings
USB devices connected via USB Type-A can be controlled from a PC connected to the display via USB Type-C. If USB devices such as cameras, speakers and microphones are permanently installed in the conference room, simply connect the USB Type-C cable to the PC to start the meeting immediately.
Dynamic signage possible with portrait zoom
Separate content from image sources and enlarge the display in portrait mode. No special devices, such as processors, are required to create content from different images. By placing three SQ2H models vertically, a display equivalent to 112 inches is created. This enables highly visible shop signage.

The display has an integrated 4K-compatible USB media player
When a USB stick with stored content is inserted, playback starts automatically. Thanks to 4K compatibility, digital signage in 4K quality can also be realised without a PC or set-top box. It can be played back without interrupting marker areas and black images. Content can also be switched via LAN or multiple displays can be operated.

PC software enables even easier and more convenient playback and management of content
The SQ2H series has a USB media player function that enables easy playback of signage. Content Management Software is an application software for programming the playback of digital signage on a computer. It also allows you to set Poser ON/OFF.
Automatic content playback with scheduling function
Content Management Software for PC version 3.2 (free) allows you to easily create playlists with media support, including combinations of still and video images. You can set up schedules to play and stop your media playlist at predefined dates and times.
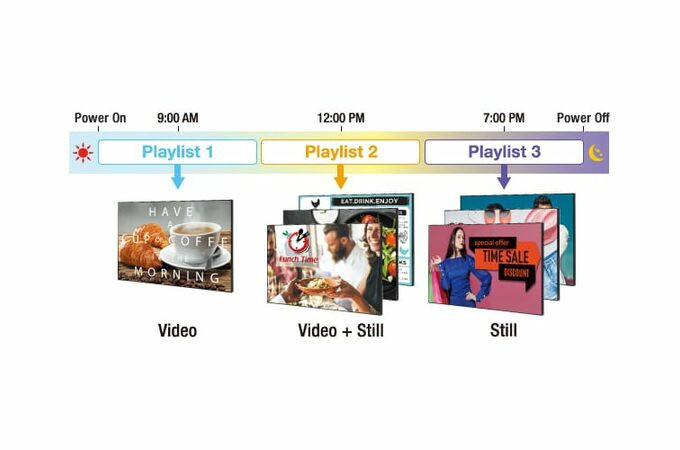
Easy synchronisation of playlists and schedules
Playlists and schedules created with the content management software can be transferred to the displays via USB memory or LAN. Synchronised playback on multiple screens is also supported.
Technical data
| Name | Panasonic TH-43SQ2HW 43" Display |
|---|---|
| Article number | 1000031666 |
| GTIN/EAN | 4010869319584 |
| Manufacturer SKU | TH-43SQ2HW |
| EPREL ID | 1592088 |
| Model name | TH-43SQ2HW |
| Brand | Panasonic |
| Product Type | Non-Touch Display |
| Technology | LCD |
| Panel type | VA |
| backlight | Direct-LED |
| Resolution | 3840 x 2160 4K UHD |
| Diagonal | 43" |
| Aspect Ratio | 16:9 |
| Viewing angle - Horizontal | 178° |
| Viewing angle - Vertical | 178° |
| Contrast Ratio | 1,200 :1 |
| Max. Brightness | 700 cd/m² |
| run-time | 24/7 |
| Response time | 8ms |
| Refresh Rate | 60Hz |
| Haze Level | 25% |
| Support - VESA | 200 x 200 |
| Frame width | 13.9 mm |
| Inputs | 1x 3,5mm Jack , 1x RS232 , 1x USB-C , 1x VGA , 2x USB-A , 3x HDMI |
| Outputs | 1x 3,5mm Jack |
| Features | HDMI-CEC , Integrated media player , Integrated speaker , Portrait Mode |
| Product width | 97.3 cm |
| Product height | 56.2 cm |
| Product depth | 6.5 cm |
| Weight | 11.5 kg |
| Colour | Black |
| EEK Spectrum | A to G |
| Energy efficency class | G |
| Delivery contents | Power cable , Remote control |
| Condition | New |
| Warranty | 36 Month |
| Warranty type | Onsite Repair Service and support information |
Downloads
Product safety
| Person responsible for the EU |
|---|
| Panasonic Deutschland |
| Winsbergring 15 |
| 22525 Hamburg |
| Germany |
| panasonic.de@eu.panasonic.com |



